Generating T-Pose Models in 3D: Techniques and Benefits
In the 3D world, character modeling and animation, the T-pose is an essential concept that serves as a foundational state for creating dynamic and lifelike characters. This pose, characterized by a figure standing upright with arms extended horizontally, is a universal standard in the industry for rigging and animation processes. T-pose allows artists and animators to work more efficiently and effectively, ensuring that characters can move smoothly and realistically in various scenarios. Understanding the significance of T-pose models is crucial for aspiring 3D artists and animators, as it underscores the importance of structure and consistency in creating engaging digital performances.
In this blog today, we will explore “T-Pose Models in 3D: Techniques and Benefits”.
What is T-Pose?
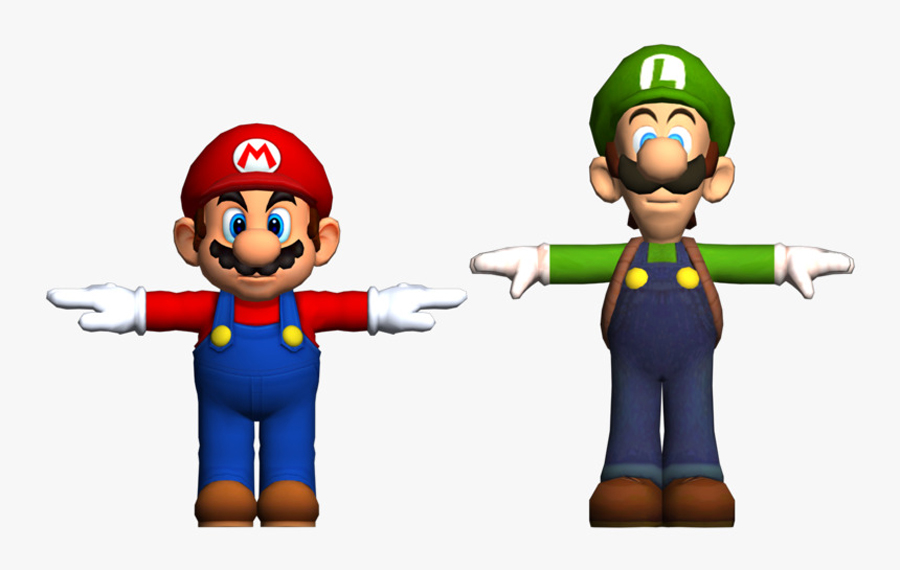
Mario in T-Pose
The T-pose is a foundational stance used in 3D modeling and animation, characterized by a character standing upright with arms extended horizontally to the sides, forming a “T” shape. This neutral position is essential for rigging, as it provides a symmetrical and balanced base from which animators can define the skeletal structure of the character. By starting with a T-pose, artists can ensure that movements are realistic and fluid when transitioning to dynamic actions like walking or jumping. The T-pose has become a standard practice in the animation and gaming industries, facilitating collaboration across teams and tools, as it streamlines the process of applying animations and textures. Overall, the T-pose serves as a critical reference point, enabling the creation of lifelike digital performances in various artistic disciplines.
When to use a T-Pose Model?
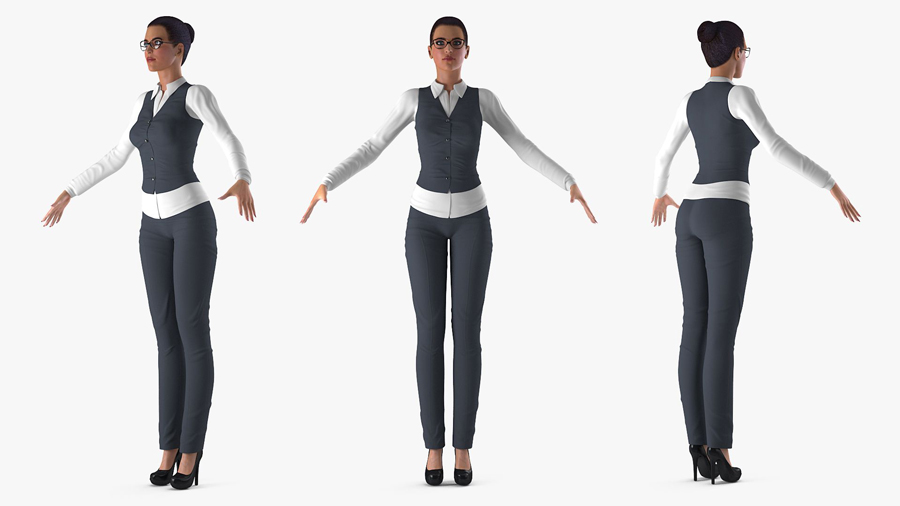
Image Source: Free 3D
A T-pose model is essential during several key stages of 3D character creation and animation. Initially, it is used during the modeling phase to establish a baseline for the character’s proportions and anatomy, allowing artists to sculpt and detail the model with clarity. During the rigging process, the T-pose provides a neutral stance that simplifies the alignment of the skeletal structure, ensuring proper joint placement for subsequent animations. It also serves as the default stance from which animators create and test various movements, facilitating smooth transitions between animations and maintaining consistency. Furthermore, when exporting models to game engines, using a T-pose ensures compatibility and streamlines the animation workflow, as many engines recognize it as a standard initial state.
Importing and Rigging Animation
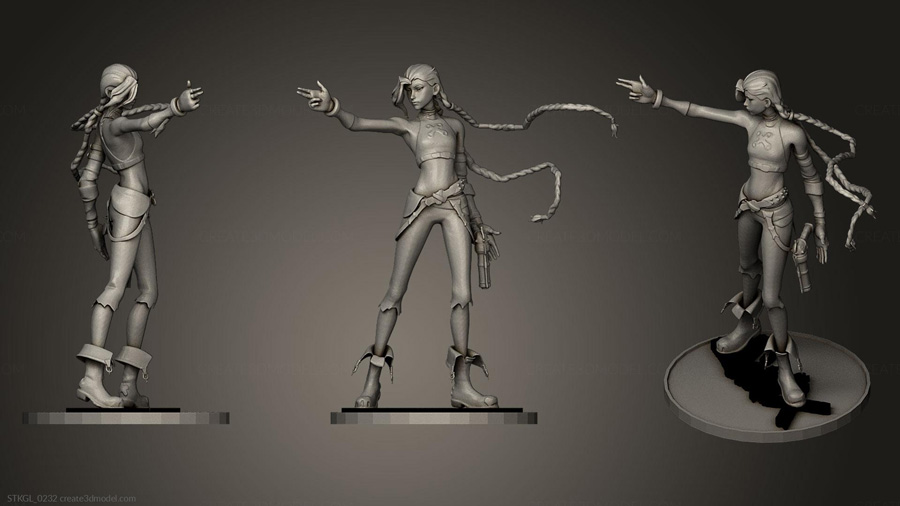
Image Source: Create 3D Model
Importing and rigging a 3D character model in a T-pose is a vital step in the animation workflow, facilitating the character’s preparation for movement. The process begins with importing the model into 3D software, ensuring it is in a compatible file format. Once imported, it’s essential to verify that the character is properly positioned in a T-pose, with arms extended horizontally. Following this, a skeleton is created to match the character’s anatomy, establishing a hierarchy of bones to ensure natural movement. The next step involves skinning the model, which includes binding the mesh to the bones through weight painting, allowing the software to determine how different parts of the mesh should deform when the corresponding bones are animated. After the rig is completed, it is crucial to test the setup by posing the character in various positions, including returning to the T-pose to ensure accurate deformations. Any necessary adjustments to weights or bone placements should be made based on the testing results. Once the rigging is finalized, the model is prepared for animation, allowing animators to create smooth and lifelike movements starting from the T-pose.
Common Alternatives to the T-Pose (A-Pose and Relaxed Poses)
While the T-pose is a widely recognized and commonly used stance in 3D modeling and animation, several alternatives can also be employed depending on the project’s specific requirements. Two notable alternatives are the A-pose and relaxed poses.
A-Pose
The A-pose is characterized by the character standing upright with arms raised slightly from the sides, forming an “A” shape. This pose can be advantageous for rigging as it provides a clearer view of the geometry for the shoulders and upper body, reducing issues like shoulder twisting that can occur in a T-pose. The A-pose can help facilitate natural deformations when the character is animated, making it particularly useful for humanoid characters where shoulder movement is critical. Additionally, the A-pose may better suit certain character designs or stylistic choices, offering a balance between a neutral stance and dynamic motion.
Relaxed Poses
Relaxed poses involve positioning characters in a more natural, casual stance rather than in a strict, symmetrical pose. This can include having arms at the sides with a slight bend or placing one leg forward to suggest weight distribution. Relaxed poses can be beneficial for characters that are designed for specific types of animation, such as idle or conversational animations. Using a relaxed pose for rigging can help in capturing more organic movements when transitioning to animations, as it more closely resembles how people typically stand or move in real life.
Choosing Between Poses
The choice between T-pose, A-pose, and relaxed poses often depends on the specific needs of a project, the character’s design, and the intended animation style. For example, T-poses are still prevalent for their standardization in the animation industry, while A-poses can offer practical advantages for certain rigging needs, and relaxed poses can enhance the realism of character motion. Ultimately, selecting the most appropriate pose is critical for achieving smooth and effective animations, ensuring that the character performs convincingly in its environment.
Applications of the T-Pose in 3D Workflows
Image Source: Freepik
The T-pose is a crucial element in various stages of 3D workflows, particularly in the realms of character modeling, rigging, and animation. It serves as the default stance for creating character models, allowing artists to focus on proportion and anatomy while ensuring the model is correctly aligned and scaled. During the rigging process, the T-pose facilitates the accurate placement of bones within the character, particularly in the shoulders and arms, which minimizes issues related to joint rotation and deformation during animations. For animators, the T-pose acts as a foundational starting point for creating idle animations and transitioning into dynamic movements, ensuring smooth and believable character animations. In game development, many engines, such as Unity and Unreal Engine, recognize the T-pose as the standard state for character models, streamlining the import process and ensuring seamless animation integration within the game environment. Additionally, the T-pose aids in testing and validation phases, allowing developers to evaluate rigging accuracy and animation fluidity easily. It also promotes collaboration and documentation within teams, providing a standardized reference point that enhances communication among modelers, riggers, and animators.
Conclusion
T-pose models are fundamental to the 3D asset creation pipeline, serving as a critical reference point throughout various stages, including modeling, rigging, and animation. As the default stance for character creation, the T-pose allows artists to develop accurate proportions and anatomy, ensuring that characters are visually coherent and properly aligned. Additionally, T-pose models streamline the workflow in game development and animation production, as they are widely recognized within industry-standard software and game engines, enabling seamless integration into projects.
Using T-Pose Modes in the newest card 4090 at iRender
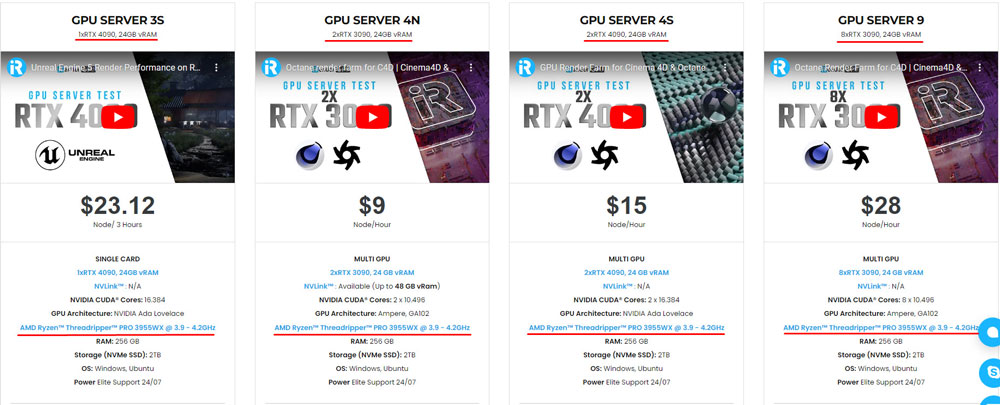
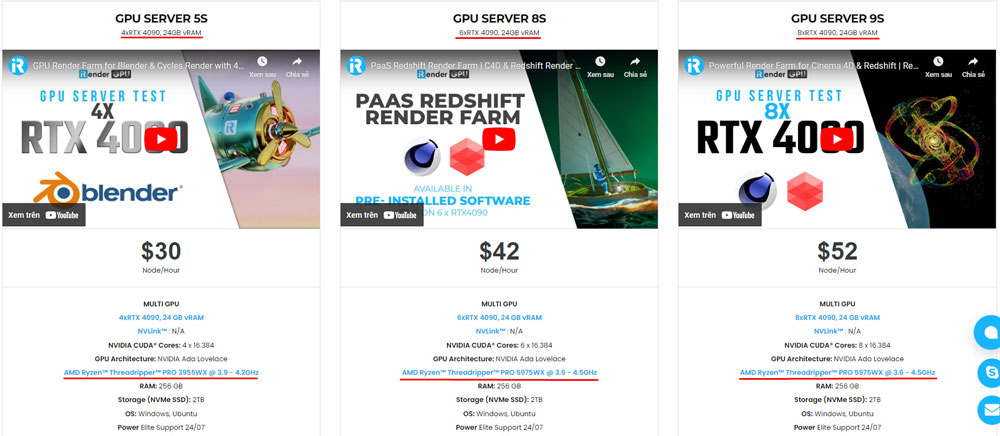
iRender Farm provides high-configuration servers that increase CPU and GPU rendering speeds. Right now, we offer from 1/2/4/6/8 RTX 4090s and 8 RTX 3090 servers. All servers at iRender are also equipped with AMD Ryzen™ Threadripper™ PRO 3955WX @ 3.9 – 4.2GHz or AMD Ryzen™ Threadripper™ PRO 5975WX @ 3.6 – 4.5GHz, 256GB RAM, 2TB Storage NVMe SSD.
You can check all our servers with its configuration here:
Besides, you also can watch some our test video on RTX 4090 card:
Besides, we also have flexible prices for all small to big projects. Don’t forget we still have big promotion in this month:
Enjoy our high end GPU now and boost your multiple GPUs rendering now! If you have any comments about our article, please do not hesitate to reach us at [email protected] or Whatsapp: +(84) 916017116.
iRender – Happy Rendering!
Related Posts
The latest creative news from Blender Cloud Rendering.