How to choose the best GPU for Gaming and Rendering in 2024
GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is at the heart of visual performance, influencing everything from frame rates in the latest video games to the speed and quality of 3D rendering in various applications. With so many available options, understanding a GPU’s key features and specifications is essential to making an informed decision.
In this blog today, we will explore how to choose the best GPU for Gaming and rendering in 2024. We will consider important factors when choosing a GPU, including performance benchmarks, VRAM capacity, thermal efficiency, compatibility with your system, and future-proofing your investment. Whether you’re a dedicated gamer seeking immersive graphics, a professional renderer requiring quick rendering times, or a casual user wanting a balanced experience, we’ll help you navigate the options to find the best GPU that fits your specific needs.
Overview of GPU
Image Source: Medium
The Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed to accelerate the processing of images and videos. Initially developed for rendering graphics in video games and other visual media, GPUs have evolved significantly and now play a crucial role in various computational tasks beyond graphics, such as machine learning, scientific simulations, and data analysis.
At its core, a GPU functions by handling parallel processing tasks, which allows it to perform many calculations simultaneously. This is in contrast to a Central Processing Unit (CPU), which is optimized for sequential processing and general-purpose tasks. The architecture of a GPU is designed to handle multiple operations on large datasets, making it particularly effective for rendering complex images and handling high-resolution graphics.
The primary function of a GPU is to render graphics for games and applications, translating data into visual output that can be displayed on monitors. This involves processing vertices, applying textures, and calculating lighting effects. A typical GPU consists of thousands of small processing cores, specialized memory, and a high-speed memory interface. The architecture can vary significantly based on the manufacturer (such as NVIDIA or AMD) and the intended use case, whether for gaming, professional rendering, or scientific research.
Key factors to consider when choosing GPU
Performance: Processing Power, Core Count, Clock Speed
Processing Power
Image Source: New Atlas
Unlike CPUs, which are versatile general-purpose computing units adept at managing a wide range of tasks, GPUs are specifically engineered for massively parallel processing. They excel in executing numerous concurrent threads—often in the tens of thousands—on lightweight threads designed for fine-grained parallel tasks.
The number of cores is crucial for rendering, which relies significantly on parallel processing. Technologies like NVIDIA’s CUDA cores and AMD’s Stream Processors are examples that facilitate this parallelism in tasks such as 3D rendering.
Core Count
A100 Core (Image Source: NVIDIA)
Core count is a critical metric in assessing a GPU’s performance, particularly for applications that rely heavily on parallel processing, such as rendering and gaming. A higher core count allows the GPU to execute numerous threads concurrently, significantly enhancing its ability to handle complex calculations associated with graphics rendering. This parallelism is essential for managing the vast amounts of data involved in tasks like shading, texture mapping, and light simulation, enabling smoother frame rates and improved visual fidelity. In modern rendering engines, which are often optimized for multi-threading, more cores translate to faster processing times, allowing for detailed scenes with intricate effects to be rendered efficiently. Additionally, as software evolves and demands more computational power, having a GPU with a higher core count ensures better performance in next-generation applications. Thus, the core count of a GPU plays a pivotal role in determining its capability to deliver high-quality graphics and real-time rendering performance.
Clock Speed
Image Source: Versus
For example, Nvidia’s RTX series is very famous currently with high CUDA core counts which makes it suitable for professionals. Clock speed is a fundamental aspect of GPU performance that refers to the frequency at which a GPU’s cores operate, measured in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz). Higher clock speeds typically enable a GPU to perform more calculations per second, which can enhance its overall processing power and responsiveness in various applications. In rendering, for instance, increased clock speeds can lead to faster frame rates and improved rendering times, as each core can execute instructions more rapidly. However, it is important to consider that clock speed alone does not determine performance; the architecture of the GPU, including its core count and memory bandwidth, also plays a significant role.
Memory: VRAM Capacity and Speed
VRAM Capacity
VRAM capacity, or Video RAM capacity, is a critical determinant of a GPU’s performance, particularly in graphics-intensive applications such as gaming, 3D rendering, and video editing. VRAM serves as a high-speed memory buffer that stores textures, frame buffers, and graphical data, enabling the GPU to access this information quickly during processing. A larger VRAM capacity allows for handling more complex textures and higher resolutions. Insufficient VRAM can lead to performance degradation, including stuttering, longer loading times, and reduced frame rates, as the GPU may need to access slower system memory when it runs out of dedicated graphics memory.
VRAM Speed
The speed of VRAM determines how swiftly data can be read from or written to the graphics memory, impacting the GPU’s ability to handle high-resolution textures and complex graphical computations. If the VRAM speed is insufficient relative to the GPU’s processing capabilities, it can create a bottleneck, diminishing performance and leading to lag or stuttering during gameplay or rendering. Therefore, alongside VRAM capacity, VRAM speed plays a crucial role in ensuring that a GPU can efficiently manage the demands of modern graphics workloads.
Compatibility
Today GPUs tend to be quite large, so it’s important to ensure that your PC case has enough space to fit them. Additionally, the dimensions of the GPU itself are crucial, so always verify that it is compatible with the available space in your case. GPUs also require a significant amount of power, so it’s essential to check that your power supply unit (PSU) can deliver sufficient wattage to support the GPU as well as the other components in your system.
Software Support
Image Source: Tech Bang
GPU drivers serve as the communication bridge between the operating system and the hardware, translating high-level commands from software into low-level instructions that the GPU can execute. Regularly updating these drivers is crucial, as manufacturers frequently release updates to enhance performance, fix bugs, and ensure compatibility with the latest games and graphics applications. Features such as tessellation, ray tracing, and resolution scaling rely on well-optimized software to deliver the best visual quality without compromising frame rates.
Some GPUs are specifically optimized for certain software applications. For example, Nvidia GPUs tend to perform better and are often favored for 3D rendering tasks because they offer superior CUDA support, which is the most commonly used and popular software in this field.
Price
High-performance GPUs, like the Nvidia RTX 4090 or the AMD Radeon RX 7900 XTX, offer improved performance to both professionals and gamers. Cards of this caliber can easily handle 4K gaming and complex 3D scenes. Not only that, but they are also capable of more challenging rendering tasks, hence naturally commanding a premium price tag.
For example, mid-range GPUs—the Nvidia RTX 4070 or AMD Radeon RX 7800 XT—represent an unrivaled balance of performance versus cost. This segment includes graphics processing units that are sure to drive most rendering tasks and run modern games at high settings, hence making them ideal for people who need strong performance without breaking the bank.
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing the best GPU for rendering and gaming requires careful consideration of various factors, including performance, compatibility, and budget. High-performance GPUs excel in handling demanding tasks and delivering stunning visuals, making them ideal for professionals and avid gamers alike. However, it’s crucial to assess your specific needs and workflow requirements to ensure that you choose a GPU that appropriately balances power and cost.
If you are on a tight budget but still want to own a high-end GPU for your work, let’s join in iRender Farm
iRender Farm Provides High-End GPU on the market
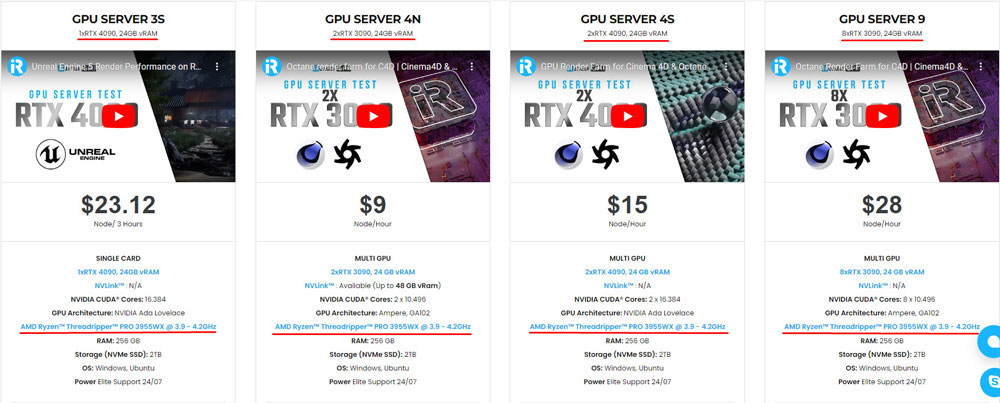
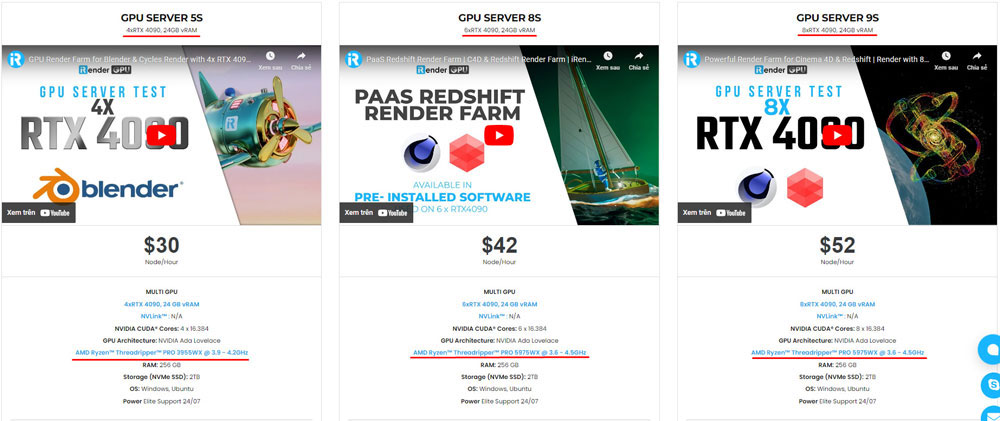
iRender provides high-configuration servers that increase CPU and GPU rendering speeds. Right now, we offer from 1/2/4/6/8 RTX 4090s and 8 RTX 3090 servers. All servers at iRender are also equipped with AMD Ryzen™ Threadripper™ PRO 3955WX @ 3.9 – 4.2GHz or AMD Ryzen™ Threadripper™ PRO 5975WX @ 3.6 – 4.5GHz, 256GB RAM, 2TB Storage NVMe SSD.
You can check all our servers with its configuration here:
Besides, you also can watch some our test video on RTX 4090 card:
Besides, we also have flexible prices for all small to big projects. Right now, we have big deals like this:
Enjoy our high end GPU now and boost your multiple GPUs rendering now! If you have any comments about our article, please do not hesitate to reach us at [email protected] or Whatsapp: +(84) 916017116.
iRender – Happy Rendering!
Related Posts
The latest creative news from Blender Cloud Rendering, Redshift Cloud Rendering, Houdini Cloud Rendering , Octane Cloud Rendering, 3D VFX Plugins & Cloud Rendering.