Should we use CPU or GPU for rendering in Blender?
Blender is a unique software for tasks like 3D modeling, animation, physics simulations, rendering, etc. Many industries use 3D modeling to create animated films, animated and non-animated game components, simulations, environments, 3D printed objects, etc. Blender has many necessary tools and add-ons to act on all the crucial tasks.
If you mainly use CPU for rendering in Blender, you must focus on the computer processor. Similarly, if you use multiple GPUs, the rendering process will depend greatly on the graphics card you use. Therefore, using CPU or GPU in Blender depends on many factors as well as the properties of each project. In this article, we will find the answer to the question: “Should we use CPU or GPU for rendering in Blender?”
The Difference between CPU and GPU rendering in Blender
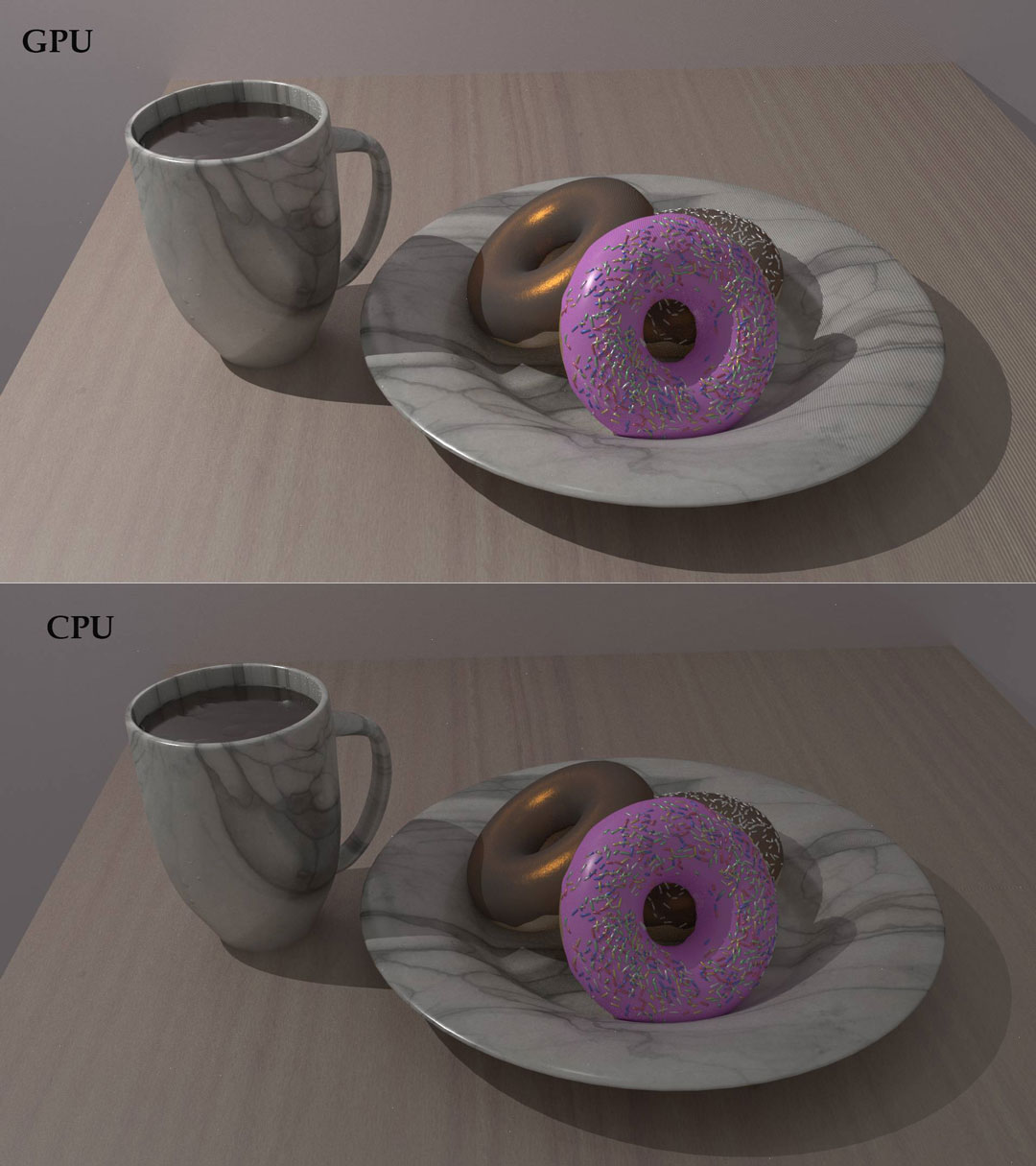
Rendering with GPU and CPU in Blender (Image Source: RogerN via Blender)
Rendering is the process of creating a two-dimensional or three-dimensional image from a model or models by application programs into a 3D image. This is a complicated process where you calculate the appearance of your scene by using your CPU and/or GPU to create a final result. Both CPU and GPU are equally important.
In Blender, we can use a lot of ray tracing and ray casting, the way light bounces about a 3D scene is quite similar to how it works in reality. Depending on the render engines you’re using, this process is handled either by your CPU (Central Processing Unit) or your GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), or both if you use hybrid render engines such as Cycles. For example, if you use Octane for Blender, or Redshift for Blender, you mainly focus on GPU rendering. In contrast, if you use WorkBench or Arnold Renderer, you will need to focus on the CPU.
CPUs are good at handling large amounts of broad information and doing it accurately in serial (one at a time), whereas GPUs are great at handling large amounts of very particular information and processing it quickly in parallel. They are both necessary to speed up the rendering process, and each is significant in its own way.
Using CPUs for rendering in Blender
CPU rendering (Image Source: gyulailevi via YouTube)
Blender is also a software that can use CPU for rendering. When performing 3D modeling, artists need to perform many different tasks such as scaling, rotating, and shaping the objects, as well as adding, merging, and removing vertices. It needs to execute predefined and user-defined calculations on the mesh. Since computer processors can easily do such calculations on 3D objects so it depends a lot on your CPU. As a result, Blender requires at least a 4-core CPU. Thanks to more cores, Blender can perform different operations on the 3D mesh simultaneously.
Blender requires at least 8 GB of RAM to complete these calculations in order to keep the necessary information and instructions for manipulating the mesh. You also prepare good hardware for smooth physics simulation, animation, and rendering of 2D images and 3D content and movies. However, if you only use CPU for rendering in Blender, it will slow down the rendering process. Because these processes need at least an 8-core CPU and 8 GB of RAM. That is the reason why you can switch to using GPU in Blender for fast processing. Since Blender can use multiple GPUs, you will need powerful enough hardware to handle the most complex tasks in Blender.
Using GPUs for rendering in Blender
Cycles GPU in Blender (Image Source: Techgage)
GPU rendering is the process of utilizing one or multiple graphics cards to render 3D images. Blender can use multiple GPUs. Multiple GPUs come into play during rendering with Cycles, but not in Eevee. You can take advantage of GPU utilization if you use Blender with a third-party render engine such as Redshift or Octane render. Performance is the main benefit of using the GPU for rendering. If your GPU supports Cuda, Optix, or OpenCL then it will probably render more quickly than the CPU.
You will see significantly improved render times if you use multiple GPUs for rendering. As each GPU will display a part or tile of an image. For example, having two GPUs allows two tiles to be displayed at the same time. In practice, this can improve performance by 60% – 90% for render times. Please note that having two graphics cards does not double the amount of video memory allocated for rendering. It only doubles the processing power to generate the render. You can refer to our video testing Blender on server 2xRTX4090 here:
How to switch from CPU to GPU in Blender?
You can easily switch from CPU to GPU for rendering in Blender and other processing tasks. Blender supports multiple GPUs. However, when you switch, please make sure your current GPU is compatible with the Blender version. Otherwise, switching can cause errors and performance issues.
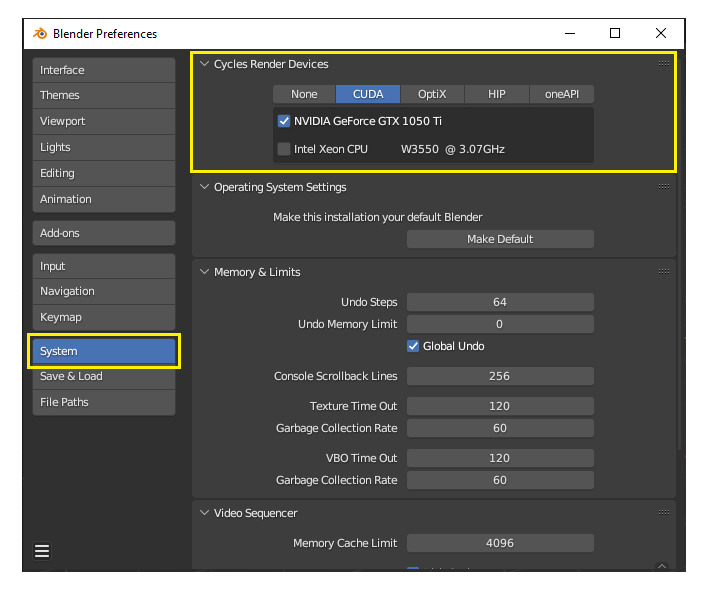
Firstly, you need open the “Edit” menu and select the “Preferences” option. After that, a small window will appear then you select “System” from that list to proceed to the next step. Next, select the “CUDA” option from the list at the top of this window under “Cycles Render Devices.”
Image Source: Blender
Switching from CPU to GPU will speed up your rendering as a graphics card has thousands of cores compared to a computer processor.
Please go to “Render Properties” then enter the “Rendering Mode” and select “Render Engine” to be “Cycles.” Next, change the “Device” from “CPU” to “GPU Computer.” It will enable your graphics card to carry most of the rendering load.
Should we use CPU or GPU for rendering in Blender?
There are some advantages to using GPU rendering over CPU rendering in Blender. GPUs are substantially better at 3D rendering than CPUs due to their optimization for graphics computations and parallel processing. If you use multiple GPUs in Blender, you are able to process many tasks simultaneously. Unlike CPUs which operate serially. GPU has thousands of cores and readily outperforms other rendering devices since rendering may be done in parallel by shooting rays, sampling pixels, or simply rendering individual frames in a sequence. So we should use GPU for rendering in Blender for best results.
Render Multiple GPUs in Blender with iRender Farm
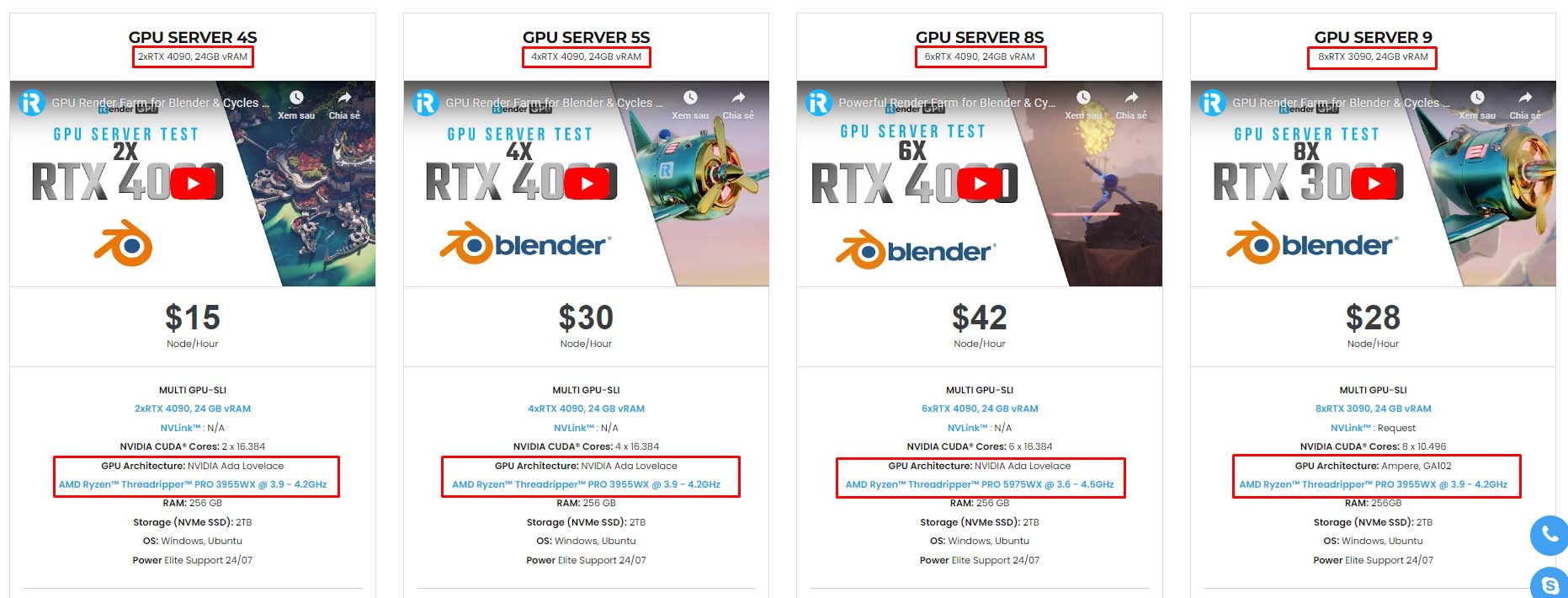
iRender provides high-performance GPU rendering services to create many wonderful scenes in Blender. We offer many configurations from 1/2/4/6/8 RTX 3090/RTX4090s for Blender rendering. Almost our servers are powered by powerful AMD Ryzen™ Threadripper™ PRO 3955WX @ 3.9 – 4.2GHz. Especially, our server 8S (6xRTX 4090) has AMD Ryzen™ Threadripper™ PRO 5975WX @ 3.6 – 4.5GHz can handle even the most demanding Blender scenes. No matter what engine you use, you can find the best option at iRender.
Check out Blender rendering performance on our 6x RTX 4090 server powered by AMD Ryzen Threadripper PRO 5975WX:
Start rendering now and bring your creativity to the world!
iRender – Thank you & Happy Rendering
References Source: Blender, CG Director, Techgage, Gyulailevi, RogerN via Blender
Related Posts
The latest creative news from Blender Cloud Rendering.