Understanding of Fluid Effects in Maya with iRender
Autodesk Maya is a powerful software widely used in the animation industry to create stunning visual effects. One of the most impressive features of Maya is its ability to simulate realistic fluid effects. You may make your animations more visually appealing and engaging by adding fluid effects, which give them a dynamic and alive quality. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the world of fluid effects in Autodesk Maya, Fluid Effects in Maya provides a wide range of tools and features to create fluid effects such as water, smoke, bubbles, and more in a 3D environment. Using these tools, users can produce dynamic and realistic fluid effects within their scenes.
In the blog, iRender will talk about Fluid Effects in Maya.
Generel information on Fluid Effects in Maya
Maya Fluid Effects is a technology for realistically simulating and rendering fluid motion. Fluid Effects lets you create 2D and 3D atmospheric, pyrotechnic, space, and liquid effects. You can use the Fluid Effects solvers to simulate these effects or fluid-animated textures for more unique, distinguishing effects.
Fluid Effects also includes an ocean shader for creating realistic open water. You can float objects on the ocean surface and have those objects react to the motion of the water.
You can create the following types of effects with Fluid Effects:
- Realistic atmospheric effects, such as clouds, mist, fog, steam, and smoke.
- Pyrotechnics, such as fire, explosions, and nuclear blasts.
- Viscous fluids, such as molten lava and mud.
- Open water, such as calm or rough oceans with white caps and foam.
Types of fluids
In Maya, there are three basic types of fluid effects:
Dynamic fluid effects
Dynamic fluid effects in Maya refer to a feature that allows you to create dynamic fluid effects such as flowing water, smoke, or mist using physics forces and fluid dynamics calculations. These can be applied to create impressive and realistic scenes for film or animation.
Non-dynamic fluid effects
3D fluids inherently require extra data to define them, which can make them very large. This extra data can slow a dynamic simulation exponentially because more calculations (solving) must be performed at every step of the simulation. For a less memory-intensive effect, you can use a 2D fluid (with less data), or you can create a non-dynamic fluid.
Oceans and Ponds
You can create Ocean and Pond fluids to simulate large realistic water surfaces, such as stormy oceans with foam and swimming pools. Oceans are NURBS planes with ocean shaders assigned to them. Ponds are 2D fluids that use a spring mesh solver and a height field.
The components of a fluid
Fluid containers
A fluid container is a rectangular 2D or 3D boundary that defines the space in which the fluid exists. Fluid effects cannot exist outside a container. The fluid container is the principle component for any dynamic or non-dynamic fluid effect. Open water effects do not require containers. For details, see Open water effects.
2D containers
A 2D fluid container is a 3D fluid container with a depth of one voxel. The size of that voxel is determined by the Z size of the container.
3D containers
A 3D fluid container is a fluid container with a depth of two or more voxels.
How to create Fluid Effects in Maya
Create dynamic fluid effects
When you play the simulation, Maya applies the fluid dynamics solver to the values in the container, calculating new values at each time step and replacing old values in the grid with the new ones.
For examples of basic dynamic fluid effects, see Fluid Effects Lessons One and Three in Getting Started with Maya. You can also load the examples in the Fluid Examples folder in the Content Browser – see Import Fluid examples.
To create a dynamic fluid effect:
- Create a fluid container. See Fluid containers.
- Add Density values to a dynamic grid. See Add properties to grids.
- Select the container, and click the fluidShape tab in the Attribute Editor:
- Set the Contents Method for Velocity to any setting but Off.
- Add Temperature and Fuel values to the container, if you are using them in the simulation. (Temperature and Fuel can be used for explosion and burning effects.)
- Add color to the fluid. See Add color to fluids.
Let’s see an example video to create a dynamic fluid effect
Create non-dynamic fluid effects
In non-dynamic fluid effects the fluid property values are predefined within Maya and stay constant over time, which means they don’t have to be recalculated. You create the appearance of the fluid by texturing a special fluid shader that is built-in to the fluid. This shader is built into the fluid for better performance.
For an example of a basic non-dynamic fluid effect, see Fluid Effects Lesson Two in Getting Started with Maya. You can also load the examples in the Fluid Examples folder in the Content Browser – see Import Fluid examples.
To create a non-dynamic fluid effect
- Create a fluid container. See Fluid containers.
-
Add them as a predefined gradient of values. Add Density values to the container that cannot change over time.
-
Add color to the container using the built-in fluid shader. See Color fluids using shading color.
-
Texture the contents of the fluid using the built-in fluid texturing capabilities. See Texturing fluids
-
To create motion, keyframe the Texture Time attribute in the Textures section of the fluid Shape Attribute Editor.
Wrap Up
In conclusion, understanding fluid effects in Autodesk Maya can open up a world of creative possibilities and career opportunities. If you want to work in animation, games, television, or film, being proficient in fluid effects techniques will help you stand out as a talented animator with a distinct artistic vision.
iRender - Maya’s best cloud rendering service
iRender is the greatest choice for your Maya pipeline whether you’re searching for a render farm or cloud rendering solution. You can use the remote workstation(s) that we offer at iRender just like a regular computer.
iRender provides high-configuration dedicated servers (physical computers/machines) specifically optimized for GPU rendering. Using our service, you will completely control the server(s) you rent through the Remote Desktop application. Therefore, you can customize your creative working environment as you wish. In short, iRender’s server is like your computer in the cloud accessible on any device instantly. You will use its full power for everything. iRender provides useful features to help you switch among the server’s configurations without having to reinstall anything. You can even run multiple servers simultaneously to speed up the renders, not having to re-install anything, either.
Maya often come with third render engines like Redshift, Octane, V-Ray, Arnold, etc.. Whether or not you use any of those render engine, you still can find a suitable package at iRender. Especially, if you use Maya with Redshift, you can access our remote servers and use our Redshift license for free. For Maya, please install and use your license to render yourself.
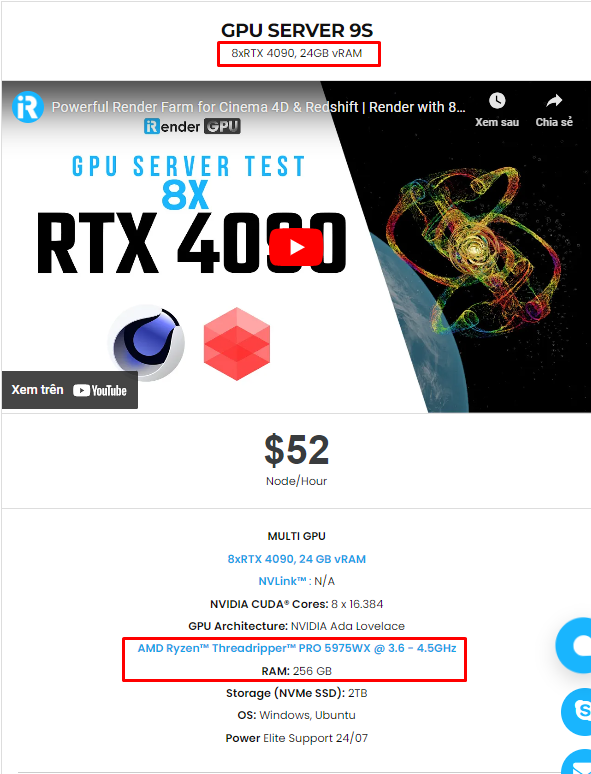
Recently, we have released our server 9S (8 card 4090). You can refer its configuration here. It is the iRender’s latest powerhouse server:
Let’s check out the rendering performance of Maya on our RTX 3090 servers.
In case you have any problems or questions, don’t hesitate to contact the 24/7 support team. We will be happy to help you with your questions and problems at all times.
This month, we are running a SPECIAL OFFER: 100% Additional Bonus for new clients who register an account and make a top-up within 24 hours after their registration.
Register an account today to experience our service or contact us via the email [email protected] or WhatsApp: (+84) 912075500 for advice and support.
Related Posts
The latest creative news from Maya Cloud Rendering, Redshift Cloud Rendering, Cinema 4D Cloud Rendering , 3D VFX Plugins & Cloud Rendering.