Understanding the dedicated and shared GPU memory
Have you ever wondered what dedicated and shared GPU memory in the Task Manager mean and what their purposes are? This article will explain everything.
What is the GPU?
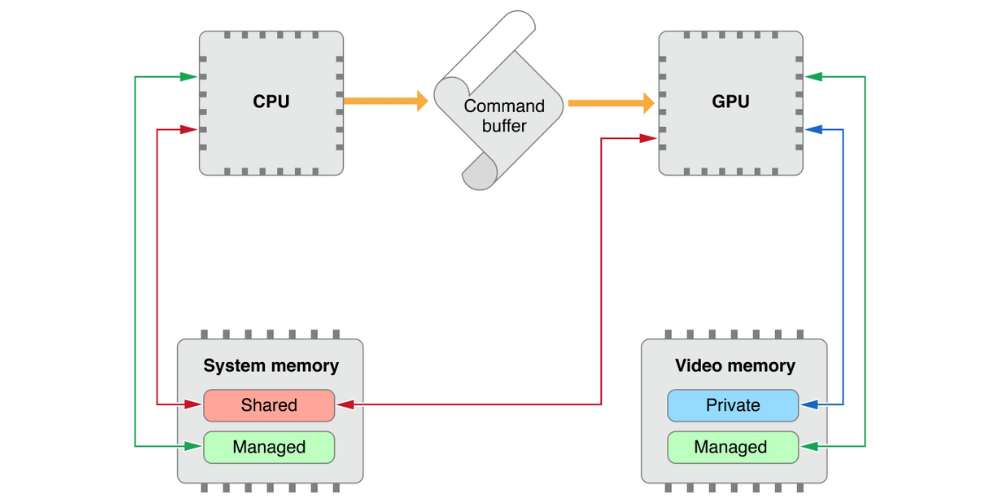
In a computer, the CPU and GPU are two essential components that work together to keep the system running efficiently. The graphics processing unit (GPU) handles graphics-related tasks, while the central processing unit (CPU) manages all other non-graphics operations.
There are two types of GPUs: integrated and discrete. Integrated GPUs are built directly into the CPU chip and rely on the shared memory from the CPU. These are typically used for basic tasks like web browsing and document editing, consuming less power and generating less heat. On the other hand, discrete GPUs are separate processing chips with their own dedicated memory, known as VRAM, along with shared memory allocated from the CPU’s RAM.
What is RAM and VRAM?
RAM, or Random Access Memory, is located on the motherboard and serves as a computer’s short-term memory. It is actively used when systems are running, browsers are open, and applications are in use. RAM allows for quick access to frequently used data, ensuring the system remains fast and responsive, especially during multitasking. In modern systems, RAM typically ranges from 8 GB to 64 GB and can be much more, but tasks like 3D CPU rendering may require significantly more, depending on the scene’s complexity.
VRAM, or Video RAM, is located on the graphics card and is specifically designed for faster read and write speeds to handle graphical data such as textures, meshes, and shaders in gaming, design software, video editing, and 3D rendering. Unlike RAM, VRAM has a modest capacity range, usually between 4 GB and 24 GB. Additionally, expanding VRAM is costly because it is fixed to the graphics card, meaning an upgrade requires replacing the entire graphics card.
The key difference between dedicated and shared GPU memory
Dedicated GPU memory
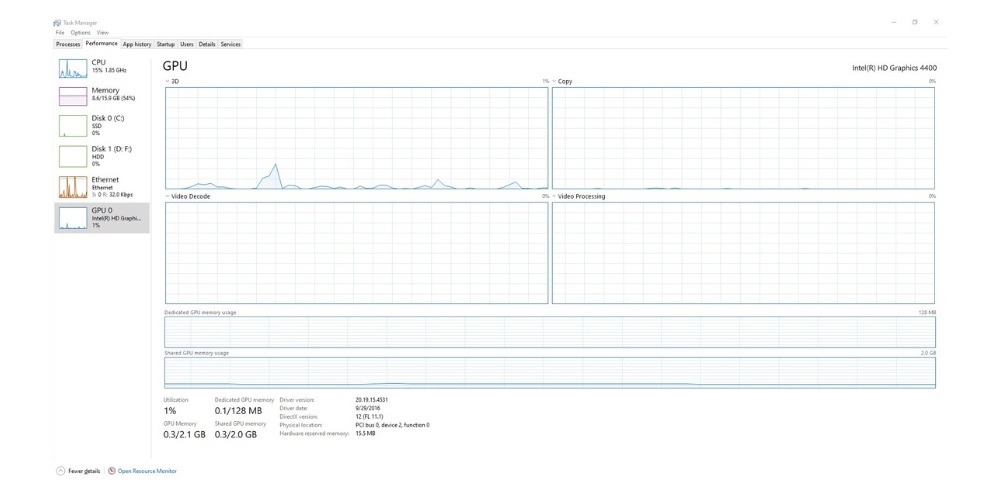
For integrated GPUs, the dedicated GPU memory displayed in the Task Manager is typically much smaller than the system’s RAM. For example, as shown in the image above, the Intel(R) HD Graphics 4400 has only 128 MB of dedicated GPU memory, whereas the Intel(R) Core(TM) i3-4150 CPU comes with 16 GB of RAM. Although the dedicated GPU memory’s capacity is small, for everyday tasks, GPU memory is rarely utilized since 8–16 GB of RAM is usually sufficient.
In the case of discrete graphics cards, the dedicated GPU memory refers to VRAM. For the GPU to efficiently handle tasks such as processing multiple lighting elements, shading, and enhancing textures in AAA games or 3D rendering, it requires a larger amount of VRAM. For example, it needs 8GB+ VRAM for 1440p/4K gaming, 16GB+ VRAM for complex modeling and rendering. The capacity of VRAM typically ranges from 4 GB to 24 GB. Currently, the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 is considered a high-end graphics card, equipped with 24 GB of VRAM.
Shared GPU memory
To prevent system crashes when dedicated GPU memory is fully utilized, a portion of RAM is allocated as shared GPU memory. This shared memory not only acts as a backup for VRAM but is also used during data exchange between the GPU and CPU.
However, relying on shared GPU memory can slow down processing speed, potentially leading to screen lag and FPS drops. There are two primary reasons for this: first, the GPU must transfer data to shared memory via PCIe connectors, which requires additional time and effort. Second, shared GPU memory is essentially system RAM, which doesn’t function as efficiently as VRAM when handling graphical tasks. Additionally, this process can increase power consumption and the likelihood of thermal throttling, as the system works harder to manage the excess graphical workload.
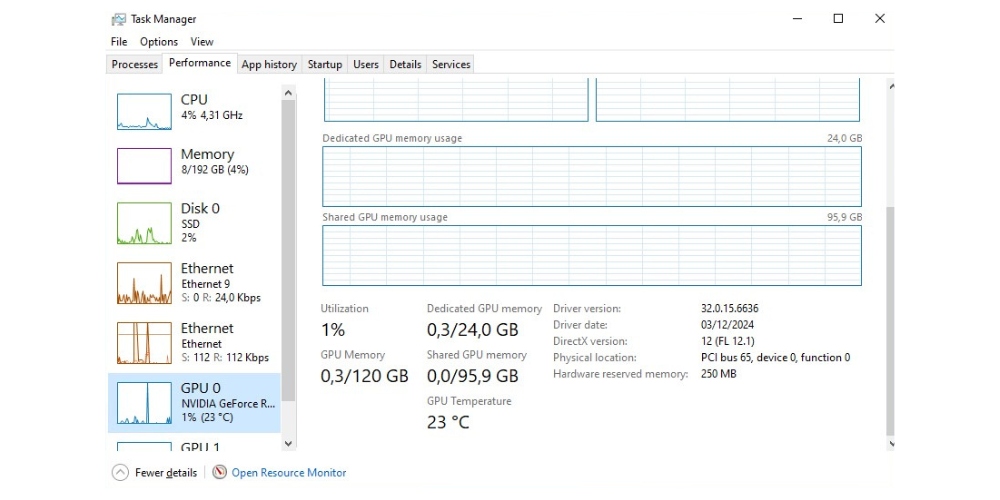
Despite these drawbacks, shared GPU memory remains a crucial component for maintaining system functionality. The more the better. As shown in the screenshot above, iRender’s 2xRTX 3090 machine includes 95.9 GB of shared GPU memory, 24 GB of dedicated GPU memory, and 256 GB of RAM, no need to worry about running out of Dedicated GPU memory or lacking of Shared GPU memory anymore.
iRender’s machines - Enhancing the rendering performance
No more worry about running out of dedicated GPU memory, iRender provides high-configuration machines with upmarket specifications: high-end GPUs including 1/2/4/6/8 x RTX4090 or RTX3090 24 GB with strong CPUs such as AMD Ryzen™ Threadripper™ PRO 3955WX @ 3.9 – 4.2GHz or AMD Ryzen™ Threadripper™ PRO 5975WX @ 3.6 – 4.5GHz, RAM 256GB, and Storage NVMe SSD 2TB, which can dramatically enhance the speed of rendering. Most importantly, we always update to the latest GPU technology.
Why can iRender be a great render farm for you?
In addition to high-configuration servers, iRender provides many other utilities to provide the best user experience.
- Dedicated server for individuals: You have full control and access to the server you rent. The working environment (installed apps, files) will be stored for the next use.
- Easy and free file transfer between your computer and iRender’s server: The transferring task can be done via iRender GPU application for Windows and the iRender Drive application for MacOS.
- 24/7 assistance: iRender’s attentive agents are always ready to support all your queries.
- All software compatibility: iRender’s PCs are built to meet the configuration needs of all 3D software and rendering tools at various cost levels for users to choose from.
Let’s see how our servers work!
HOT DEAL: 100% bonus for new users
New users will get a 100% bonus for the first transaction within 24 hours of their registration. No minimum amount!! If you top up $50, you will get 100 points in total to hire our machines.
If you have any questions, please contact me through email [email protected] or our 24/7 support team for a quick response.
Thank you for reading & Happy Rendering!
Source: Intel, Reddit, Supoeruser, EasyPC, Electronics Hub
Cover image source: cgdirector
Related Posts
The latest creative news from Tutorial