Advantages and Disadvantages of CPU and GPU Rendering in Blender
When it comes to rendering in Blender, one of the necessary decisions you’ll face is whether to use your CPU (Central Processing Unit) or GPU (Graphics Processing Unit). Both options offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, making the choice important for optimizing rendering times and overall efficiency. This blog dives deep into the pros and cons of CPU and GPU rendering, providing you with a comprehensive understanding to make an informed decision tailored to your specific project needs and hardware capabilities. By exploring these aspects, you can explore the full potential of Blender and streamline your rendering workflow.
Let’s get started!
Advantages and Disadvantages of CPU Rendering in Blender
Advantages
CPU (Central Processing Unit) rendering in Blender involves utilizing the computer’s main processor to generate the final image. While GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) rendering has gained prominence due to its speed advantages, CPU rendering remains a viable and, in some cases, preferable option. CPUs are renowned for their precision in calculations, ensuring highly accurate and reliable results. This accuracy is particularly beneficial when dealing with scenes that require precise lighting, shadows, and reflections. Moreover, CPUs can effectively manage scenes with high polygon counts, advanced effects, and intricate simulations due to their robust processing capabilities. They are less prone to running into memory limitations when handling extremely large and detailed scenes. Additionally, one more thing is that CPU rendering is generally more compatible with a wider range of Blender features, plugins, and rendering engines. It ensures consistent performance across different hardware configurations and software versions.
Disadvantages
Despite its advantages, CPU rendering also has notable drawbacks that should be considered. CPUs are generally slower at rendering images compared to GPUs due to their sequential processing nature. This can significantly increase the time required to complete rendering projects, especially for animations and high-resolution images. CPUs are not specifically designed for visual data processing, making them less efficient for rendering-intensive tasks. They lack the specialized hardware and parallel processing capabilities of GPUs, resulting in slower performance. Rendering on the CPU can consume a significant amount of system resources, potentially impacting the performance of other applications running simultaneously. Also, CPUs are not well-suited for real-time rendering applications, such as game development and interactive visualizations. Their slower processing speeds and lack of specialized hardware make it difficult to achieve the required frame rates for smooth real-time performance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of GPU Rendering in Blender
Advantages
GPUs can significantly reduce rendering times compared to CPUs due to their parallel processing capabilities. This speed advantage is particularly noticeable when rendering complex scenes with high polygon counts and advanced effects. Designed specifically for graphics and image processing, GPUs are highly efficient at handling the calculations required for rendering. They excel at tasks such as ray tracing, shading, and texture mapping, resulting in faster and more efficient rendering performance.
The specific GPU model used has a significant impact on rendering speed and efficiency. Higher-end GPUs with more CUDA or OpenCL cores and larger VRAM capacities generally deliver better performance in Blender.
As Blender can use multiple GPUs for rendering, it can increase speed and reduce rendering time. You can add more GPUs to increase rendering power which allows for faster completion of complex projects. Distributes the rendering workload, preventing any single GPU from being overloaded.
Disadvantages
GPUs have limited video memory (VRAM), which can be a bottleneck when rendering extremely complex scenes with high-resolution textures. If the scene exceeds the available VRAM, Blender may resort to using system memory, which can significantly slow down the rendering process. Besides, GPU performance is heavily dependent on having the latest and most stable drivers. Therefore, outdated or incompatible drivers can cause crashes, errors, or reduced performance.
Key Factors to Consider
Several factors should be considered when choosing between CPU and GPU rendering in Blender:
- Scene Complexity: Assess the complexity of your scene. For scenes with intricate details, high polygon counts, and advanced effects, a CPU might be more reliable due to its accuracy and memory handling. In contrast, simpler scenes can benefit from the speed of GPU rendering.
- Hardware Specifications: Evaluate the specifications of your CPU and GPU. A high-end GPU with a large amount of VRAM will likely outperform a mid-range CPU in rendering tasks. Conversely, a powerful CPU with sufficient RAM can handle complex scenes that might overwhelm a lower-end GPU.
- Rendering Engine: Different rendering engines in Blender, such as Cycles and Eevee, utilize hardware resources differently. Cycles tends to benefit more from GPU rendering due to its path-tracing algorithm, while Eevee is a real-time engine that can utilize both CPU and GPU.
- Project Requirements: Consider the specific requirements of your project. For animations or tasks where speed is critical, GPU rendering can significantly reduce production time. For architectural visualizations or product renderings where accuracy is paramount, CPU rendering might be the preferred choice.
- Budget: Take your budget into account. High-end GPUs can be a significant investment, while upgrading a CPU might be a more cost-effective solution depending on your existing hardware.
Benchmarking and Testing
Currently, the overall fastest CPU for Blender depends on your specific workflow. Modeling and animation tasks are better on a single, fast core. While rendering is better with large numbers of cores. Simulations are somewhat split. Cloth and rigid body simulations only use a few fast cores, while fluid simulations will use lots of cores.
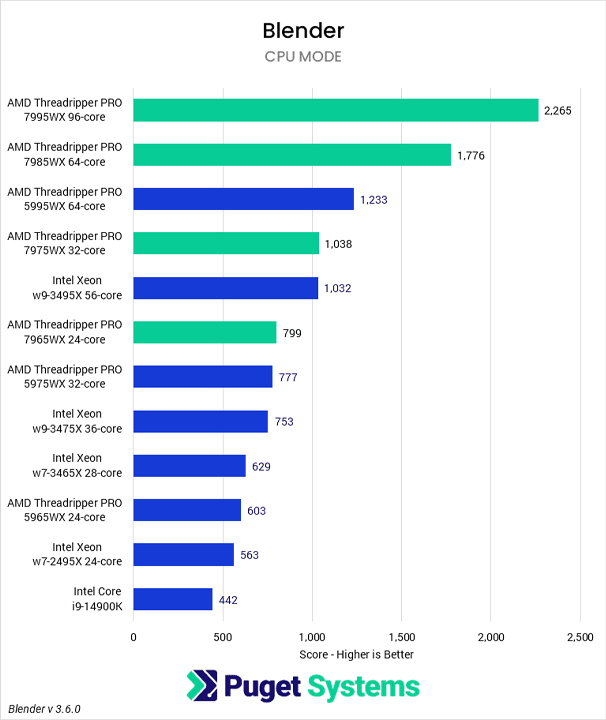
If you will be doing a lot of fluid simulations, or relying on CPU rendering, then the current fastest CPU is AMD’s Threadripper™ 7995WX. It offers 96-cores, and support for up to a massive 1TB of RAM.
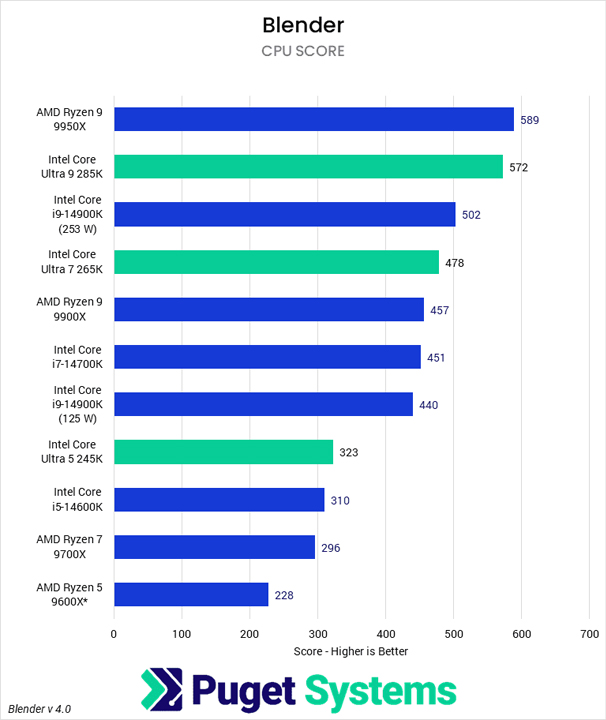
If you are primarily interested in modeling and animation, the AMD RyzenTM 9000 Series and Intel CoreTM Ultra CPUs are the ideal choices. Higher core count models like the Ultra 9 285K and Ryzen 9 9950X will provide superior CPU-based rendering if necessary, while lower core count models like the Core Ultra 7 265K and Ryzen 7 9700X are more reasonably priced.
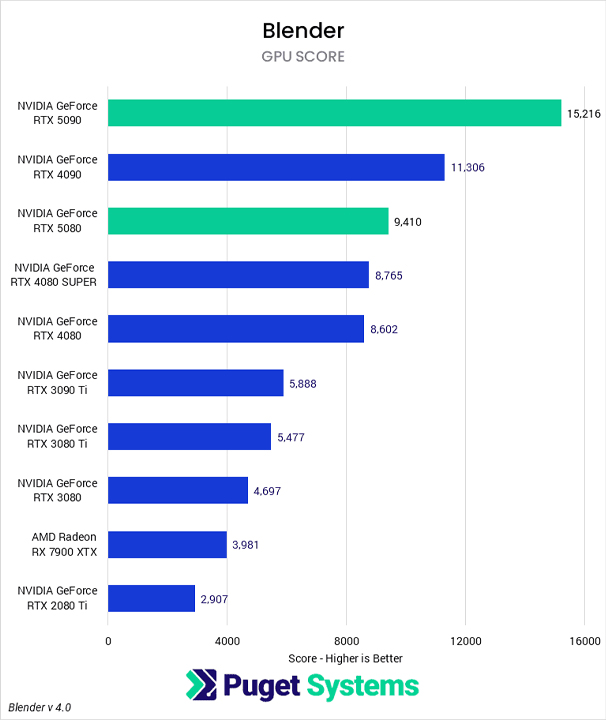
The fastest GPU for Blender is the NVIDIA GeForce RTX™ 5090. The other RTX 40 & 50 Series cards also perform quite well. Let’s take a look this benchmark following:
Hybrid Rendering
In some cases, the ideal solution is to use both the CPU and GPU simultaneously through hybrid rendering. Blender allows you to configure Cycles to utilize both your CPU and GPU, distributing the rendering workload and potentially achieving faster rendering times than either processor could manage on its own. By utilizing both the CPU and GPU, Blender can distribute the rendering workload and potentially reduce rendering times compared to using only one processor. Hybrid rendering allows Blender to take advantage of all available computing resources, maximizing efficiency. When dealing with scenes that have both high complexity and high polygon counts, the CPU can handle the complex calculations while the GPU accelerates the rendering of visual elements.
How to Enable Hybrid CPU and GPU Rendering in Blender:
- Open Blender’s Preferences: Go to Edit > Preferences.
- Access System Settings: Navigate to the System tab.
- Select Render Devices: Under “Cycles Render Devices,” you will see options for your CPU (typically named “CPU”) and GPU (e.g., “CUDA”, “OptiX”, “HIP”, “oneAPI”, “Metal”).
- Enable Both: Check the boxes next to both your CPU and GPU to enable them for rendering.
Is CPU or GPU better for rendering in Blender?
There’s no definitive “better” option between CPU and GPU rendering in Blender. The ideal choice depends on your specific circumstances. CPU rendering offers accuracy, stability, and the ability to handle extremely complex scenes that might exceed GPU memory.
GPU rendering is generally faster for most tasks due to its parallel processing capabilities. It’s especially efficient for visually intensive tasks. In many cases, using multi GPUs can work in parallel, reducing the time it takes to render images or animations. This is particularly beneficial for complex scenes where every second counts. With multiple GPUs, Blender can improve viewport rendering performance, facilitating smoother interactions and real-time updates even in complex scenes. This allows for more efficient modeling and scene composition. Therefore, if you want to improve your render’s performance, you can consider GPU rendering.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both CPU and GPU rendering have their respective advantages and disadvantages, and the optimal choice depends on the specific demands of your project and workflow. For many users, a hybrid approach that utilizes both CPU and GPU rendering can provide the best of both worlds, depending on the scene complexity and rendering requirements. Ultimately, understanding your hardware capabilities and the nature of your projects will guide your decision in choosing the most effective rendering method in Blender.
Speed up your Blender projects with iRender
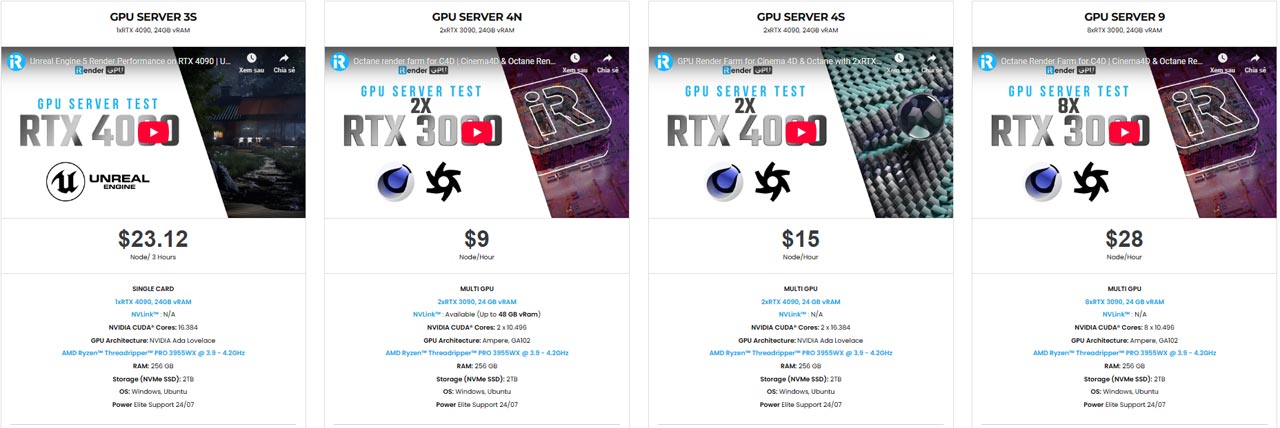
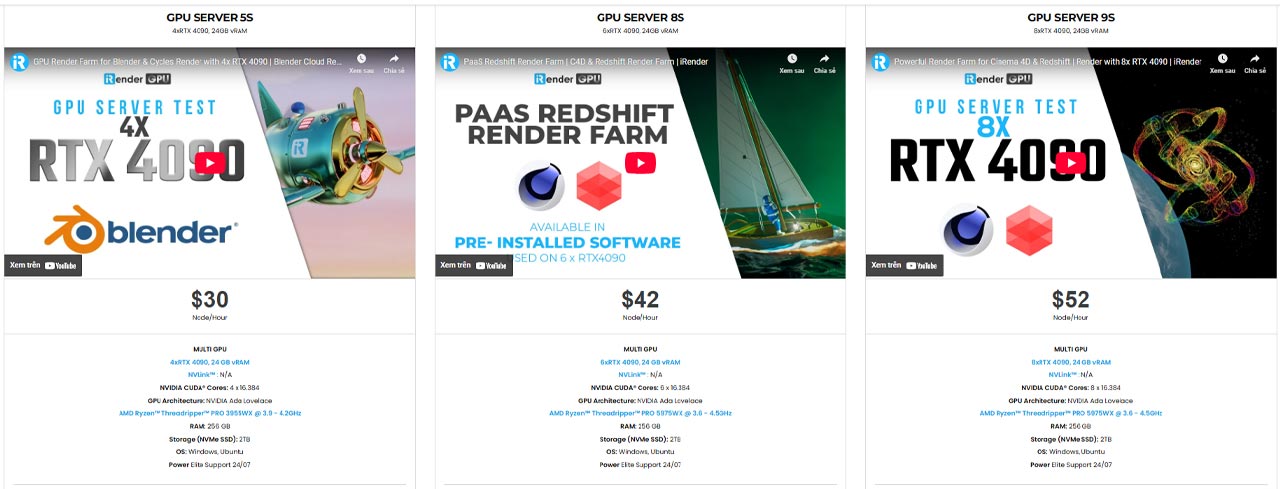
iRender is proud to be one of the best GPU service providers on the market. You can find a lot of options suitable for your Blender project. iRender offers from 1/2/4/6/8 RTX 4090s and 3090s. In addition to offering powerful configurations, all servers at iRender are also equipped with AMD Ryzen™ Threadripper™ PRO 3955WX @ 3.9 – 4.2GHz or AMD Ryzen™ Threadripper™ PRO 5975WX @ 3.6 – 4.5GHz, 256GB RAM, 2TB Storage NVMe SSD. The high-end configuration is extremely suitable for complex Blender projects.
Our machine has preinstalled Blender 4.4.1, you can easily create and then connect to it then you set up your own working environment and render yourself as you do on your own computer. You can have a look at our configuration and our tutorial video following:
Let’s see how our RTX4090 performs when rendering with Blender scenes:
Why Choose iRender?
At iRender, we pride ourselves on providing unparalleled cloud rendering services designed to enhance your creative workflow. With our high-end GPU configurations, user-friendly interface, and dedicated support, it’s easier than ever to achieve stunning results.
IaaS Infrastructure – Full Control & Customization
iRender operates on an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) model, providing powerful GPU servers while allowing you to install software, plugins, and customize your workflow freely.
GPU Power- RTX 4090/3090
We provide access to high-performance GPU servers designed specifically for rendering. You can choose between single or multiple GPUs depending on your project needs.
Outstanding Support
In case you have any problems or questions, don’t hesitate to contact the 24/7 support team. We will be happy to help you with your questions and problems at all times.
- 50% BONUS for all transactions from $230
- 100% BONUS for all transactions from $575
Register an account today to experience our service or contact us via email at [email protected] or WhatsApp: at (+84) 912075500 for advice and support.
iRender – Happy Rendering!
Related Posts
The latest creative news from Blender Cloud Rendering.