Consider between CUDA and OptiX for Blender cycles
When considering rendering in Blender’s Cycles engine, users with NVIDIA graphics cards are presented with two primary choices: CUDA and OptiX. Both leverage the power of the GPU to accelerate the rendering process, but they differ in their underlying technology and performance characteristics. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing rendering workflows and achieving optimal results. In this blog today, iRender will explore the features of both options, which help you make a decision between CUDA and OptiX for Blender cycles.
Let’s get started with iRender!
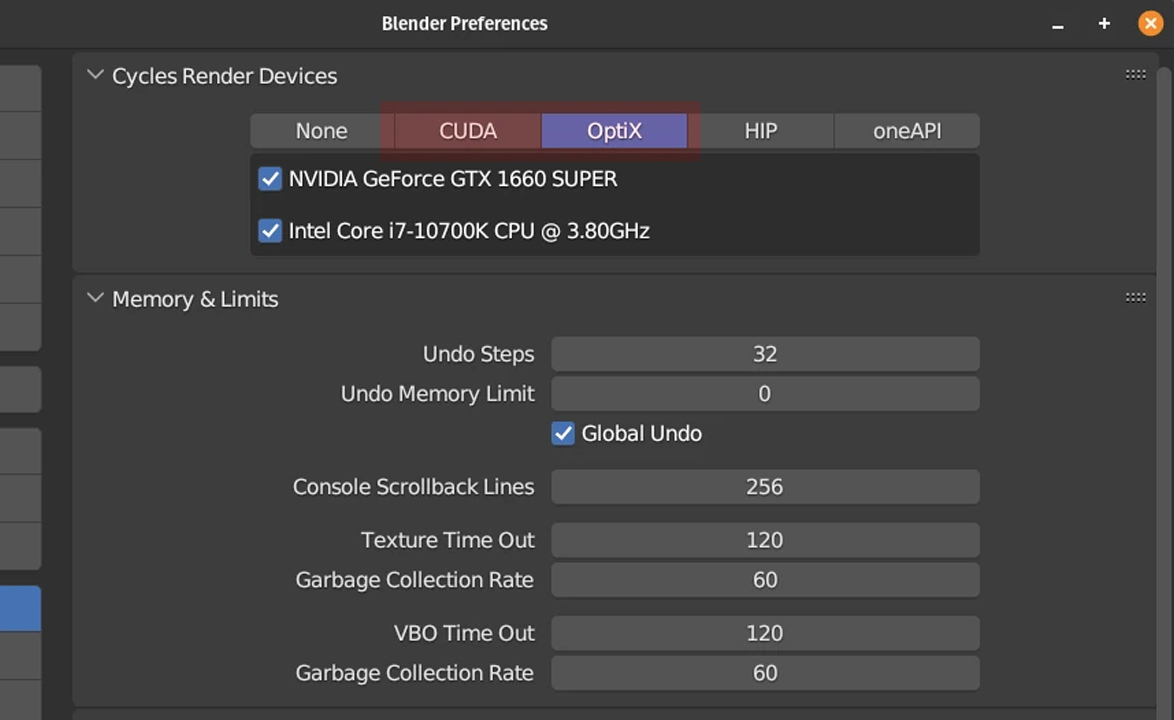
Overview of CUDA and OptiX for Blender cycles
CUDA and OptiX are both NVIDIA technologies used to accelerate rendering in Blender’s Cycles engine. They allow you to leverage the power of your graphics card (GPU) to speed up the process of creating realistic images and animations.
CUDA is NVIDIA’s parallel computing platform that allows developers to access the GPU’s power for general-purpose processing. In Blender, CUDA has long been the standard for GPU rendering, offering stable performance across a wide range of NVIDIA cards.
OptiX is NVIDIA’s ray-tracing engine that leverages RT Cores (found in RTX GPUs) for hardware-accelerated ray tracing. It’s a newer backend for Blender and is designed to deliver faster rendering by offloading more of the ray tracing computations to specialized cores on RTX GPUs.
Performance Comparison
Rendering Speed
In Blender Cycles, OptiX generally provides a significant speed boost compared to CUDA, especially when using NVIDIA RTX graphics cards. This is because OptiX is specifically designed to utilize the dedicated RT (Ray Tracing) cores on RTX cards, which dramatically accelerates ray tracing calculations. Many users and benchmarks have shown substantial reductions in render times when switching from CUDA to OptiX on RTX hardware. Some reports indicate OptiX can be 60-80% faster than CUDA.
While OptiX generally outperforms CUDA on RTX, the degree of the speedup can depend on the scene’s complexity and the extent to which it relies on ray tracing. Scenes with extensive reflections, refractions, and complex lighting tend to benefit more from OptiX’s accelerated ray tracing. For simpler scenes, the difference might be less dramatic.
Here’s a comparison table for a hypothetical complex scene with plenty of reflections and area lights that was rendered in several modes on the same RTX GPU to show performance differences:
| Mode | Render Time | Speed |
| CPU (no GPU) | 10 minutes | 1× (baseline) |
| GPU with CUDA | 1 minute 30 seconds | ~6.7× faster than CPU |
| GPU with OptiX | 1 minute | ~10× faster than CPU / ~1.5× faster than CUDA |
In summary, OptiX excels in ray-tracing-heavy scenes with RTX hardware. CUDA remains competitive for simpler renders and broader GPU compatibility.
Denoising
OptiX has a significant advantage in denoising, particularly when used with NVIDIA RTX graphics cards. This is because OptiX leverages the Tensor Cores on RTX cards for AI-accelerated denoising. This results in faster and often more efficient denoising, helping to quickly produce clean images even with low sample counts. OptiX denoising can be used for both final renders and viewport previews, significantly speeding up the interactive rendering experience.
CUDA also supports denoising in Cycles, but it does not have the same AI acceleration capabilities as OptiX on RTX cards. While CUDA can use the GPU’s general processing power for denoising, it typically won’t be as fast as OptiX on compatible hardware.
Testing and benchmark of CUDA and OptiX for Blender cycles
If your primary focus is on rendering speed and quality, particularly with more complex scenes, and you are using a modern RTX GPU, OptiX may be the better choice due to its optimization for real-time ray tracing and performance enhancements.
On the other hand, if you are using older hardware, need maximum stability, or work in a mixed hardware environment where compatibility is critical, CUDA might be the more reliable option.
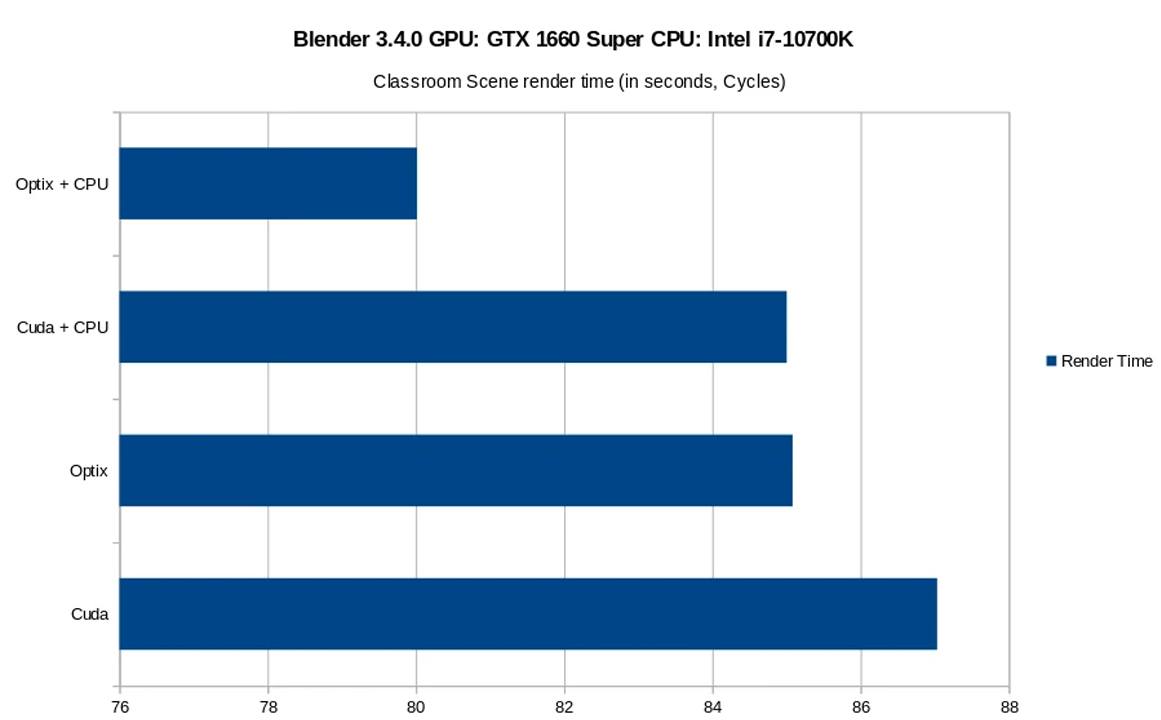
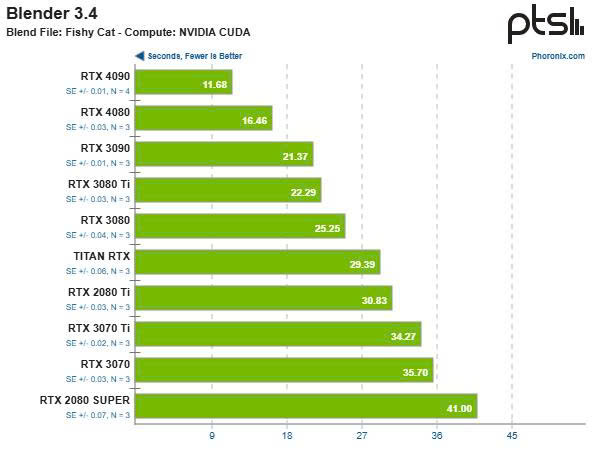
Below Bar diagram compares the rendering times for OptiX and CUDA rendering on a GTX 1660 Super GPU and an Intel i7-10700K CPU. You can also see rendering times for OptiX+CPU and CUDA+CPU.
The chart shows render times for the same scene using both CUDA and OptiX backends. From the chart, you can easily see the differences of CUDA and OptiX when render a same scene. The fastest rendering time for the Blender Classroom scene was achieved by combining OptiX and CPU, which was closely followed by CUDA+CPU, OptiX alone, and CUDA alone.
What’s more, OptiX’s real-time ray tracing capabilities make it a quicker rendering method than CUDA. OptiX and CPU together were able to outperform CUDA and OptiX alone so rendering times can still be significantly impacted by CPU processing capability.
In the performance comparison shown on the above charts, both CUDA and OptiX were tested under the same conditions using the same GPU. The results are quite clear: CUDA rendered the scene in 9.39 seconds, while OptiX completed the same task in just 5.52 seconds. This marks a significant performance improvement of over 41% when using OptiX compared to CUDA. This outcome highlights the practical benefits of using OptiX on RTX-enabled GPUs. The dedicated ray-tracing cores in these GPUs allow OptiX to handle light interactions and shadows more efficiently than CUDA, which relies on general-purpose cores. Moreover, this efficiency doesn’t come at the cost of quality—both CUDA and OptiX maintain the high rendering fidelity required for professional-level work. Given these results, users working in Blender on RTX series GPUs should strongly consider using OptiX as their default rendering backend. CUDA remains a valuable option, particularly for compatibility with older GPUs or certain add-ons, but when performance is the priority, OptiX clearly leads the way.
Hardware Considerations
CUDA
- Operating system: Windows and Linux systems are its primary platforms. Legacy macOS support extends up to version 10.13
- GPU: NVIDIA GPU with CUDA capability, starting from the Kepler architecture (2012)
- Driver: An NVIDIA graphics driver with CUDA support
- V-RAM: No fixed VRAM requirement exists for CUDA, but more memory enhances efficiency
OptiX
- Operating system: Windows and Linux exclusively, with no macOS compatibility
- GPU: RTX GPUs (Turing/2018 or newer) for full performance, leveraging RT Cores. This includes GeForce RTX 20-series, 30-series, and newer professional GPUs like Quadro RTX
- Driver: NVIDIA drivers supporting the OptiX API
- V-RAM: No fixed VRAM minimum is specified for OptiX
Conclusion
In conclusion, CUDA being a well-established framework offers broad compatibility with numerous GPU models, particularly from NVIDIA, and is a reliable option for users seeking stability and extensive support. However, OptiX, with its advanced ray tracing capabilities, leverages NVIDIA’s latest GPU architectures to significantly enhance performance, especially for complex scenes and real-time rendering tasks. Ultimately, both CUDA and OptiX provide powerful tools for rendering, and the decision should be based on the user’s hardware compatibility, specific rendering requirements, and personal workflow preferences. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each technology, Blender users can make an informed choice that best suits their projects and enhances their rendering experience.
Speed up your Blender projects with iRender
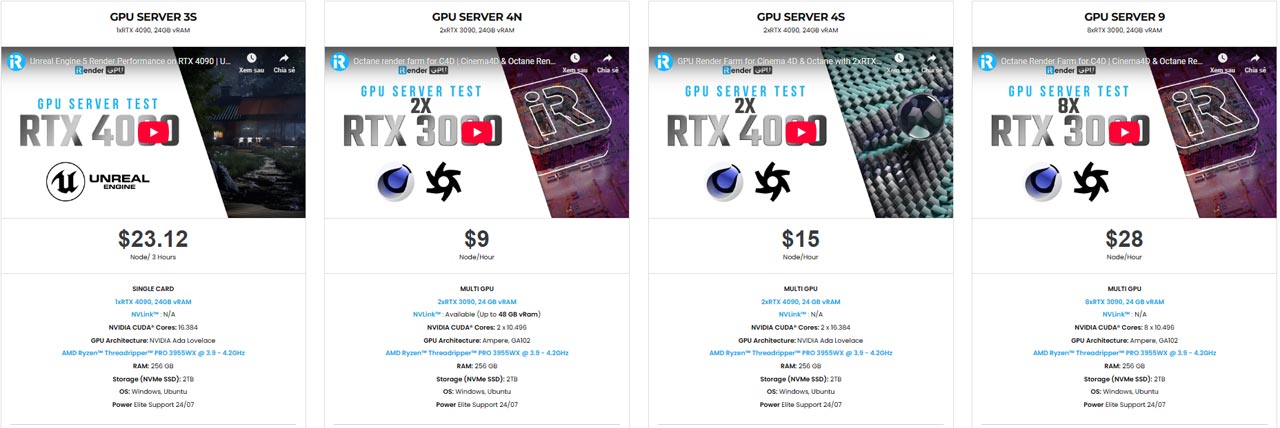
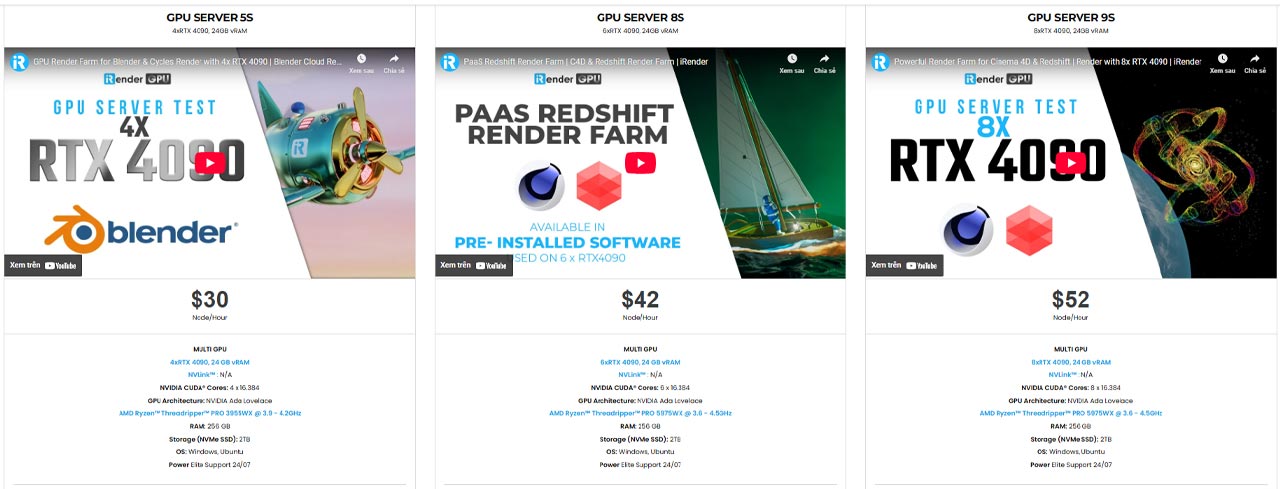
iRender is proud to be one of the best GPU service providers on the market. You can find a lot of options suitable for your Blender project. iRender offers from 1/2/4/6/8 RTX 4090s and 3090s. In addition to offering powerful configurations, all servers at iRender are also equipped with AMD Ryzen™ Threadripper™ PRO 3955WX @ 3.9 – 4.2GHz or AMD Ryzen™ Threadripper™ PRO 5975WX @ 3.6 – 4.5GHz, 256GB RAM, 2TB Storage NVMe SSD. The high-end configuration is extremely suitable for complex Blender projects.
Our machine has preinstalled Blender 4.4.1, you can easily create and then connect to it then you set up your own working environment and render yourself as you do on your own computer. You can have a look at our configuration and our tutorial video for Blender cycles following:
Let’s see how our RTX4090 performs when rendering with Blender scenes:
Why Choose iRender?
At iRender, we pride ourselves on providing unparalleled cloud rendering services designed to enhance your creative workflow. With our high-end GPU configurations, user-friendly interface, and dedicated support, it’s easier than ever to achieve stunning results.
IaaS Infrastructure – Full Control & Customization
iRender operates on an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) model, providing powerful GPU servers while allowing you to install software, plugins, and customize your workflow freely.
GPU Power- RTX 4090/3090
We provide access to high-performance GPU servers designed specifically for rendering. You can choose between single or multiple GPUs depending on your project needs.
Outstanding Support
In case you have any problems or questions, don’t hesitate to contact the 24/7 support team. We will be happy to help you with your questions and problems at all times.
- 50% BONUS for all transactions from $230
- 100% BONUS for all transactions from $575
Register an account today to experience our service or contact us via email at [email protected] or WhatsApp: at (+84) 912075500 for advice and support.
iRender – Happy Rendering!
Related Posts
The latest creative news from Blender Cloud Rendering.