Should we choose NVIDIA or AMD GPU for Redshift?
When it comes to choosing a GPU for Redshift rendering, there are two main players in the market: NVIDIA and AMD. While NVIDIA has been the dominant player for a long time, AMD has recently gained attention for its support for Redshift through its HIP platform. In this post, we’ll take a closer look at which one should we choose, NVIDIA or AMD GPU for Redshift.
Introducing AMD’s HIP
An interesting addition in this recent Redshift update is the ability to use AMD GPUs. Previously, NVIDIA has been the only GPU option for 3D rendering software due to their CUDA APIs that made it easier for developers to program and utilize the hardware. In contrast, AMD offered their own rendering solution called ProRender as a plugin for software like 3ds Max and Maya. However, that has changed recently with AMD’s HIP libraries.
HIP is AMD’s equivalent to NVIDIA’s CUDA, allowing developers to better integrate AMD hardware into their rendering engines. Blender was one of the first to incorporate HIP. Now, Maxon has integrated HIP into Redshift.
AMD HIP Ray Tracing (HIP-RT) (Source: GPUOpen)
There are two versions of HIP – standard HIP and the newer HIP-RT. Both NVIDIA and AMD’s latest GPUs have hardware-accelerated ray tracing cores. However, standard HIP does not utilize these ray tracing cores just as CUDA does not. HIP-RT will enable these ray tracing cores to help with rendering, just as NVIDIA’s RTX GPUs currently do.
This is important because when testing AMD GPUs in Redshift, NVIDIA GPUs will naturally have an edge since more of their hardware is being utilized. We need to compare performance with and without ray tracing enabled to get a better sense of how AMD GPUs actually perform in Redshift rendering. The performance comparison will be in the third section. Let us now have a look at NVIDIA’s CUDA and AMD’s HIP technologies and examine the two most powerful GPUs of each brand for Redshift, NVIDIA’s flagship RTX 4090 vs AMD’s RX 7900 XTX.
NVIDIA’s CUDA GPU vs AMD’s HIP GPU
NVIDIA’s CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) is a parallel computing platform and application programming interface (API) that provides a way to use the GPU for general-purpose computing. This platform is optimized for NVIDIA GPUs and provides excellent performance in Redshift. On the other hand, AMD’s HIP (Heterogeneous-Compute Interface for Portability) is a platform that allows developers to write code for both AMD and NVIDIA GPUs using a single source code. This platform provides a way for AMD GPUs to be used in Redshift, but the performance may not be as optimized as NVIDIA’s CUDA.
AMD’s new Radeon RX 7000 series GPUs are Team Red’s answer to NVIDIA’s RTX 40 series. NVIDIA’s current top GPU is the expensive but extremely powerful RTX 4090. AMD has two top GPUs, the RX 7900 XT, and RX 7900 XTX. How does AMD’s flagship, the XTX, compare to Nvidia’s most powerful flagship? Let’s examine:
Nvidia GeForce RTX 4090 vs AMD Radeon RX 7900 XTX
-
-
- 24 GB GDDR6X memory (faster than GDDR6)
- 76 billion transistors
- 3rd-Generation RT Cores for Ray tracing
- 4th Generation Tensor Cores for AI tasks
- 450W Power
-
-
-
- 24GB GDDR6 memory
- 58 billion transistors (-24% fewer)
- No dedicated ray tracing hardware
- No Tensor Cores
- 355W power limit (lower than RTX 4090)
-
Which is better?
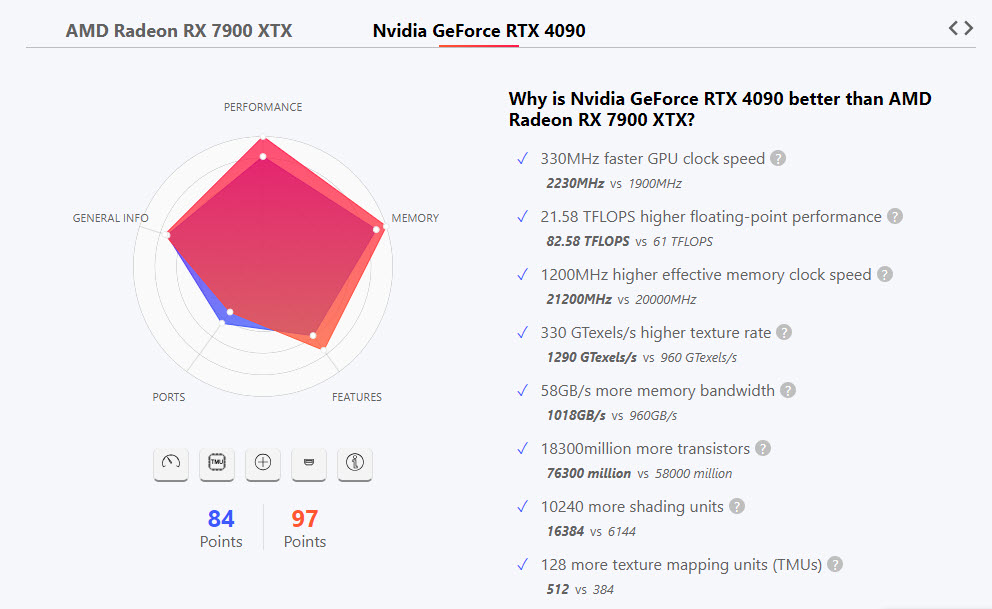
Why RTX 4090 is better than RX 7900 XTX (Source: Versus)
On paper, NVIDIA’s RTX 4090 has advantages in GPU clock speed, memory clock speed, FLOPS, texture rate, memory bandwidth, transistor count, shading units, TMUs, dedicated ray tracing cores, Tensor cores, and higher power limits.
But how does this translate to real-world Redshift performance? Let’s explore!
Performance Comparison: NVIDIA or AMD GPU for Redshift
RT Accelerated Performance (RTX Enabled)
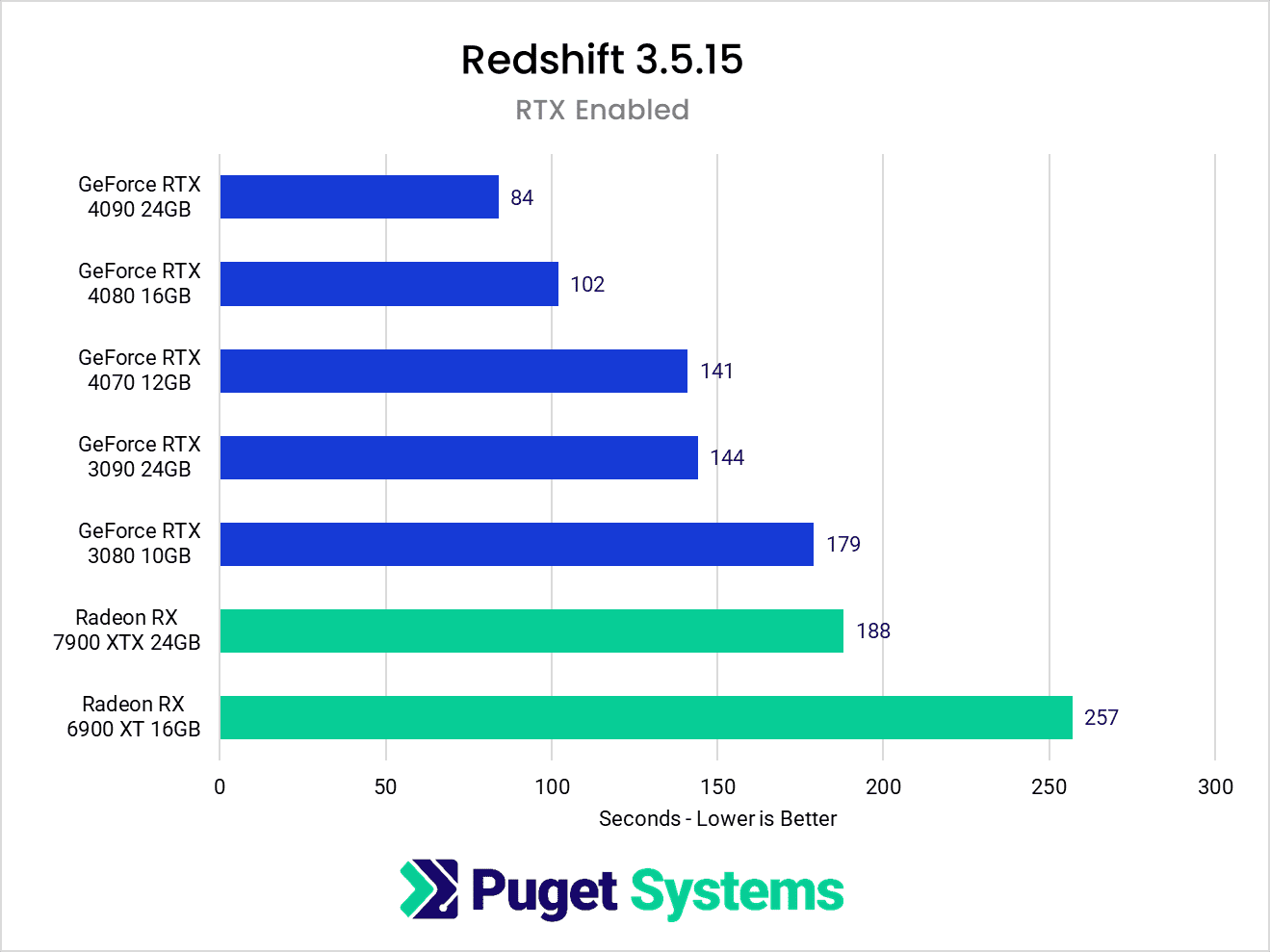
We will first compare render times using Redshift’s default settings. This allows Redshift to utilize NVIDIA’s dedicated RT cores but not AMD’s GPUs. This shows the full potential of each card at the time is this post.
Redshift 3.5.15 Performance on RTX enabled mode (Source: Puget Systems)
Based on these render times, RTX 4090 is 124% faster than RX 7900 XTX. In other words, RTX 4090 rendered the image over 2 times (124%) faster than the RX 7900 XTX. However, even at a disadvantage, AMD’s top RX 7900 XTX still comes close to matching the RTX 3080 from NVIDIA. If that were the whole story, it would still be a good result for AMD and Maxon in their first attempt at GPU rendering on Windows. NVIDIA has had years to perfect their CUDA and RTX APIs, so AMD’s keeping pace shows promise.
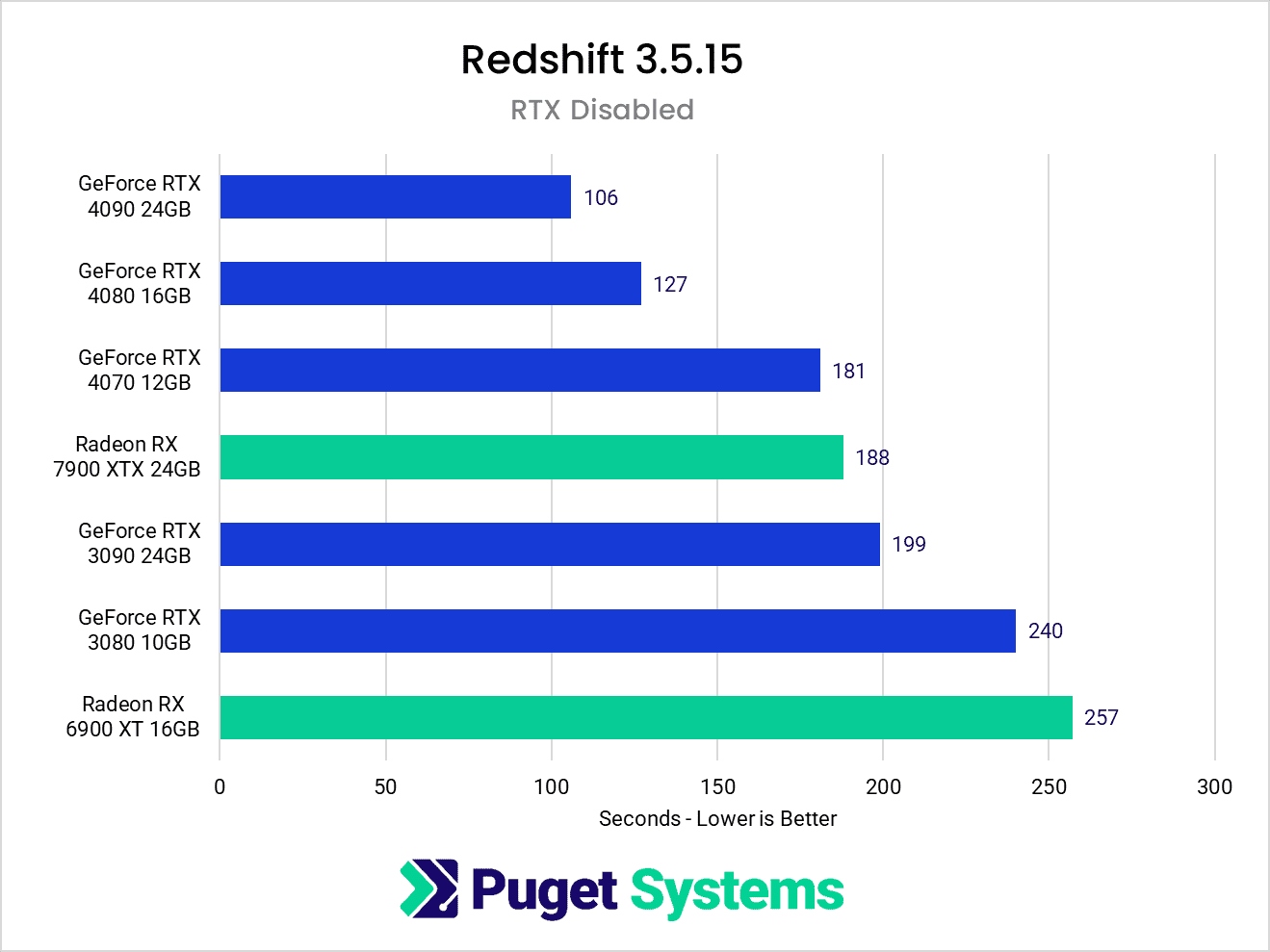
RT Disabled Performance (RTX Disabled)
Redshift 3.5.15 Performance on RTX disabled mode (Source: Puget Systems)
When testing the GPUs without using ray tracing to make it a fair comparison, the results show the 7900 XTX performing better than the RTX 3090 and coming close to the newest RTX 4070. This demonstrates that while NVIDIA still holds an edge in GPU rendering performance, AMD isn’t too far behind when ray tracing acceleration is removed from the equation.
Conclusion
The initial version of AMD hardware in the Redshift render engine is quite promising. Although AMD mainly focused on gaming performance when launching the RX 6000 and 7000 series graphics cards without much emphasis on professional content creation applications, we are now seeing AMD hardware provide good performance in the Redshift renderer. Having a large rendering program like Redshift adopting AMD support will put pressure on NVIDIA to continue innovating and improving their products.
To the question “Should we choose NVIDIA or AMD GPU for Redshift?”. A balance between Needs, Budget & Performance should be considered.
If maximum Redshift performance – especially with complex ray-traced scenes is your top priority – NVIDIA GPUs with their dedicated RT and Tensor cores are unquestionably a better choice than what AMD Radeon cards have to offer.
However, if your budget is tight or ray tracing isn’t essential, AMD Radeon cards offer a good value at around half the cost.
In summary, your specific workflow, scene complexity, and budget will determine which brand is better. NVIDIA CUDA and AMD HIP both have advantages and trade-offs. But for the outright rendering performance, NVIDIA GPUs provide a remarkably compelling option for Redshift rendering. For professionals and studios, that significant performance advantage far outweighs the lower cost of AMD cards. When your time and income depend on rendering performance, NVIDIA’s dominance in Redshift makes their GPUs worth the premium.
Render faster in Redshift with iRender
iRender provides high-performance GPU rendering services to unleash creativity for 3D artists. We offer flexible configurations of 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 GPU servers using the top-tier RTX 4090 and RTX 3090 for accelerated Redshift rendering. Powered by powerful AMD Ryzen Threadripper PRO CPUs with up to 64 cores, 256GB RAM, and 2TB NVMe SSD storage, our servers can handle even the most demanding Redshift scenes.
Best of all, we grant you complete access to your rented servers. For as little as $8.20 per hour, you can install any software, plugins, or Redshift versions you need. We treat your rented servers like your personal workstations – no restrictions apply.
This freedom enables you, 3D artists, to realize creative visions without limitations. Leverage our accelerated GPU rendering and scalable power to easily tackle CPU-intensive renders that formerly bottlenecked creativity. Say goodbye to renders taking ages and hello to rendering freedom.
Check out Redshift rendering performance on our 6x RTX 4090 server powered by AMD Ryzen Threadripper PRO 5975WX.
Make iRender your partner in creativity and unleash your potential with our high-performance GPU servers.
Start rendering today!
iRender – Happy Rendering!
Reference sources: NVIDIA, AMD, Puget Systems, Versus, GPUOpen
Related Posts
The latest creative news from Redshift Cloud Rendering.