Introduction to Data in Machine Learning
Machine learning is a form of artificial intelligence (AI) that teaches computers to think in a similar way to humans: learning and improving upon past experiences. Almost any task that can be completed with a data-defined pattern or set of rules can be automated with machine learning. Machine learning allows companies to transform processes that were previously only possible for humans to perform—think responding to customer service calls, bookkeeping, and reviewing resumes for everyday businesses. Machine learning can also scale to handle larger problems and technical questions—think image detection for self-driving cars, predicting natural disaster locations and timelines, and understanding the potential interaction of drugs with medical conditions before clinical trials. That’s why machine learning is important.
We’ve covered the question ‘why is machine learning important,’ now we need to understand the role data plays. Machine learning data analysis uses algorithms to continuously improve itself over time, but quality data is necessary for these models to operate efficiently.
To truly understand how machine learning works, you must also understand the data by which it operates. Today, we will be discussing what data in machine learning, the types of data needed for machine learning to be effective.
What is Data?
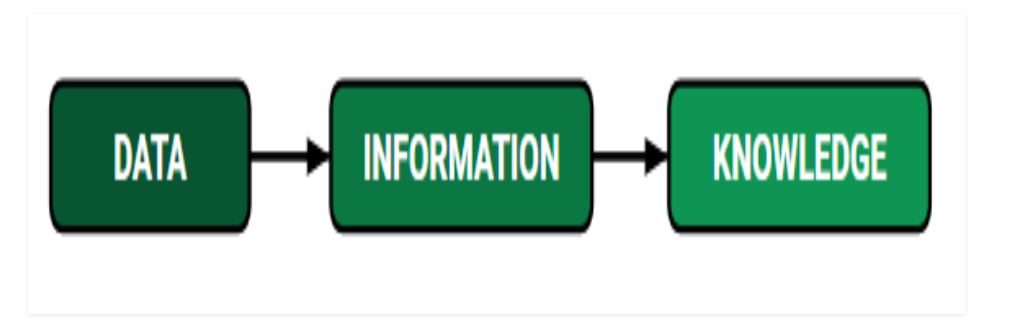
DATA: It can be any unprocessed fact, value, text, sound, or picture that is not being interpreted and analyzed. Data is the most important part of all Data Analytics, Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence. Without data, we can’t train any model and all modern research and automation will go in vain. Big Enterprises are spending lots of money just to gather as much certain data as possible.
Example: Why did Facebook acquire WhatsApp by paying a huge price of $19 billion?
The answer is very simple and logical – it is to have access to the users’ information that Facebook may not have but WhatsApp will have. This information of their users is of paramount importance to Facebook as it will facilitate the task of improvement in their services.
INFORMATION: Data that has been interpreted and manipulated and has now some meaningful inference for the users.
KNOWLEDGE: Combination of inferred information, experiences, learning, and insights. Results in awareness or concept building for an individual or organization.
What type of data does machine learning need?
Data can come in many forms, but machine learning models rely on four primary data types. These include numerical data, categorical data, time series data, and text data.
Numerical data
Numerical data, or quantitative data, is any form of measurable data such as your height, weight, or the cost of your phone bill. You can determine if a set of data is numerical by attempting to average out the numbers or sort them in ascending or descending order. Exact or whole numbers (ie. 26 students in a class) are considered discrete numbers, while those which fall into a given range (ie. 3.6 percent interest rate) are considered continuous numbers. While learning this type of data, keep in mind that numerical data is not tied to any specific point in time, they are simply raw numbers.
Categorical data
Categorical data is sorted by defining characteristics. This can include gender, social class, ethnicity, hometown, the industry you work in, or a variety of other labels. While learning this data type, keep in mind that it is non-numerical, meaning you are unable to add them together, average them out, or sort them in any chronological order. Categorical data is great for grouping individuals or ideas that share similar attributes, helping your machine learning model streamline its data analysis.
Time series data
Time series data consists of data points that are indexed at specific points in time. More often than not, this data is collected at consistent intervals. Learning and utilizing time series data makes it easy to compare data from week to week, month to month, year to year, or according to any other time-based metric you desire. The distinct difference between time series data and numerical data is that time series data has established starting and ending points, while numerical data is simply a collection of numbers that aren’t rooted in particular time periods.
Text data
Text data is simply words, sentences, or paragraphs that can provide some level of insight to your machine learning models. Since these words can be difficult for models to interpret on their own, they are most often grouped together or analyzed using various methods such as word frequency, text classification, or sentiment analysis.
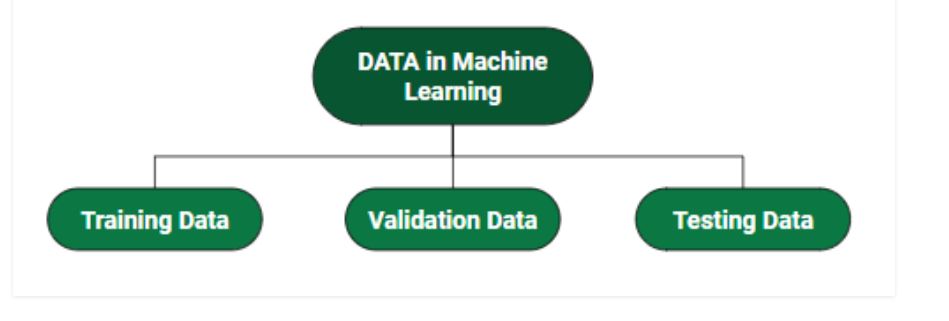
How we split data in Machine Learning?
- Training Data: The part of data we use to train our model. This is the data that your model actually sees(both input and output) and learns from.
- Validation Data: The part of data that is used to do a frequent evaluation of the model, fit on the training dataset along with improving involved hyperparameters (initially set parameters before the model begins learning). This data plays its part when the model is actually training.
- Testing Data: Once our model is completely trained, testing data provides an unbiased evaluation. When we feed in the inputs of Testing data, our model will predict some values(without seeing actual output). After prediction, we evaluate our model by comparing it with the actual output present in the testing data. This is how we evaluate and see how much our model has learned from the experiences feed in as training data, set at the time of training.
Consider an example:
There’s a Shopping Mart Owner who conducted a survey for which he has a long list of questions and answers that he had asked from the customers, this list of questions and answers is DATA. Now every time when he wants to infer anything and can’t just go through each and every question of thousands of customers to find something relevant as it would be time-consuming and not helpful. In order to reduce this overhead and time wastage and to make work easier, data is manipulated through software, calculations, graphs, etc. as per own convenience, this inference from manipulated data is Information. So, Data is a must for Information. Now Knowledge has its role in differentiating between two individuals having the same information. Knowledge is actually not technical content but is linked to the human thought process.
Properties of Data –
- Volume: Scale of Data. With the growing world population and technology at exposure, huge data is being generated each and every millisecond.
- Variety: Different forms of data – healthcare, images, videos, audio clippings.
- Velocity: Rate of data streaming and generation.
- Value: Meaningfulness of data in terms of information that researchers can infer from it.
- Veracity: Certainty and correctness in data we are working on.
Conclusion
At iRender, we provide a fast, powerful and efficient solution for Deep Learning users with configuration packages from 1 to 8 GPUs RTX 3090 on both Windows and Ubuntu operating systems. In addition, we also have GPU configuration packages from 1 RTX 3090 and 6 x RTX 3090. With the 24/7 professional support service, the powerful, free, and convenient data storage and transferring tool – GPUhub Sync, along with an affordable cost, make your training process more efficient.
Register an account today to experience our service. Or contact us via WhatsApp: (+84) 912 785 500 for advice and support.
Thank you & Happy Training!
Reference source: geeksforgeeks.org
Related Posts
The latest creative news from Cloud Computing for AI,